Время на прочтение
4 мин
Количество просмотров 17K
И снова ERROR 1040…
Техподдержка получает много жалоб на эту печально известную ошибку: ERROR 1040: Too many connections — слишком много соединений. Проблема очевидна: приложение или пользователи создают больше соединений, чем допускает сервер, то есть текущее число соединений превышает значение переменной max_connections.

Ситуация уже сама по себе проблема для конечных пользователей, но если еще при этом у вас нет доступа к серверу для диагностики и исправления причины, все становится совсем плохо. Обычно приходится завершать экземпляр и перезапускать его, чтобы восстановить.
Root-пользователь тоже не может подключиться! Почему?!
В правильно настроенной среде пользователь с привилегией SUPER сможет получить доступ к экземпляру и диагностировать причину ошибки 1040, из-за которой не хватает соединений. Это описано в руководстве:
mysqld разрешает
max_connections+ 1 клиентских соединений. Дополнительное соединение зарезервировано для аккаунтов с привилегиямиSUPER. Когда эти привилегии предоставляются администраторам, а не обычным пользователям (которым они и не нужны), администратор, у которого есть еще и привилегияPROCESS, может подключиться к серверу и использоватьSHOW PROCESSLIST, чтобы диагностировать проблемы, даже если подключено максимальное число клиентов без привилегий.
Но куча людей дают привилегии SUPER своим пользователям приложения или скрипта — из-за требований приложения (опасно!) или незнания последствий, а потом зарезервированное соединение занимает обычный пользователь, а административный пользователь (обычно root) не может подключиться.
Как гарантировать доступ к экземпляру
Можно использовать хорошо известный хак с GDB, который советовал Ауримас лет 100 назад для ошибки 1040, но теперь есть решения получше. Правда сначала их надо включить.
С Percona Server 5.5.29 и выше и MySQL 8.0.14 и выше можно настроить еще один порт с дополнительным числом соединений. Приложение не будет использовать эти интерфейсы. Они только для администраторов баз данных и агентов мониторинга и проверки работоспособности (см. примечание ниже).
Настройка Percona Server
Начиная с Percona Server 5.5.29 можно просто добавить extra_port в my.cnf, и при следующем перезапуске порт будет доступен и будет ожидать данные по тому же bind_address, что и обычные соединения. Если не настроить переменную extra_port, дополнительного порта по умолчанию не будет.
Еще можно определить extra_max_connections, чтобы задать количество подключений, которое будет обрабатывать этот порт. Количество по умолчанию — 1.
Для примера я занял все подключения к порту обычных пользователей у экземпляра, где уже настроил extra_port и extra_max_connections в my.cnf:
результат
Кстати, extra_port удален в Percona Server 8.0.14 и выше, поскольку в MySQL Community реализован admin_port с теми же функциями. Так что отредактируйте my.cnf при апгрейде до Percona Server 8.0.14 или выше, если вы уже определили extra_port.
Как я уже сказал, для этого нужен MySQL 8.0.14, где применен WorkLog 12138.
Чтобы включить админский интерфейс, нужно определить admin_addres, который должен быть единственным и уникальным (без подстановочных символов) IPv4, IPv6, IPv4-сопоставленным адресом или именем хоста, по которому админский интерфейс будет ожидать передачи данных. Если эта переменная не определена, интерфейс не включен.
Еще можно определить порт, но это не обязательно. По умолчанию это порт 33062. Если этот порт свободен, это значение не нужно настраивать. Если настраиваете, то поместите обе переменные в раздел [mysqld] в my.cnf.
Наконец, можно настроить create_admin_listener_thread (отключено по умолчанию), который создает отдельный поток для обработки входящих соединений. Это может пригодиться в некоторых ситуациях.
Еще одно различие — в документации Oracle сказано, что:
Число административных соединений не ограничено.
(А у нас значение по умолчанию — 1). Не уверен, что это значит, но я бы был осторожен, чтобы случайно не установить 1 млн соединений. Они, конечно, не ограничены, но ресурсы-то все равно потребляют.
Использование для мониторинга и проверок работоспособности
Удобно, что не только люди могут использовать дополнительный интерфейс или порт в экстренной ситуации, когда мы достигли max_connections. К нему может подключиться система мониторинга и проверки работоспособности прокси/балансировщика нагрузки/обнаружения сервисов.
Скрипты мониторинга смогут извлекать данные для диаграмм, чтобы потом вы разобрались, откуда столько соединений. А скрипты проверки работоспособности будут докладывать об ухудшившемся состоянии сервера, и определенный код может указывать, что соединений много, но сервер справляется (то есть может разобраться сам и лучше чуть дольше подождать до отработки отказа).
Обязательно устанавливайте только по одному соединению за раз для мониторинга и проверки работоспособности, чтобы не забивать extra_max_connections в Percona Server и не создать миллион потоков в MySQL. То есть скрипты не должны подключаться снова, если предыдущий запрос или подключение к базе данных еще активны.
Вот тот же пример, но с MySQL.
Для Percona Server 8.0.14 и выше процесс будет тем же, что и для MySQL Community.
Помогите! Мне нужно войти, но все порты заняты!
Если это та самая причина, по которой вы читаете этот пост, используйте безумный хак с GDB (без обид, Ауримас, просто выглядит рисково :-D) или завершите экземпляр. К счастью, экземпляр почти всегда можно аккуратно завершить с помощью SIGTERM (-15) вместо SIGKILL (-9). Так сервер выполнит чистую остановку, и у потоков будет шанс нормально завершить работу. Просто следуйте инструкциям:
1) Получите PID:
marcos.albe in ~/ pgrep -x mysqld;
6502) Отправьте SIGTERM в этот PID:
marcos.albe in ~/ kill -15 650;3) Следите в журнале ошибок, как выполняется завершение работы. Это будет выглядеть примерно так:
2019-07-11T13:43:28.421244Z 0 [Note] Giving 0 client threads a chance to die gracefully
2019-07-11T13:43:28.521238Z 0 [Note] Shutting down slave threads
2019-07-11T13:43:28.521272Z 0 [Note] Forcefully disconnecting 0 remaining clientsЭто означает начало процесса завершения работы. Экземпляр будет завершен, когда вы увидите подобную строку:
2019-07-11T13:43:31.292836Z 0 [Note] /opt/percona_server/5.7.26/bin/mysqld: Shutdown completeThis issue occurs mostly when the maximum allowed concurrent connections to MySQL has exceeded.
The max connections allowed is stored in the gloobal variable max_connections.
You can check it by show global variables like max_connections; in MySQL
You can fix it by the following steps:
Step1:
Login to MySQL and run this command: SET GLOBAL max_connections = 100;
Now login to MySQL, the too many connection error fixed. This method does not require server restart.
Step2:
Using the above step1 you can resolve ths issue but max_connections will roll back to its default value when mysql is restarted.
In order to make the max_connection value permanent, update the my.cnf file.
Stop the MySQL server: Service mysql stop
Edit the configuration file my.cnf: vi /etc/mysql/my.cnf
Find the variable max_connections under mysqld section.
[mysql]
max_connections = 300
Set into higher value and save the file.
Start the server: Service mysql start
Note:
Before increasing the max_connections variable value, make sure that, the server has adequate memory for new requests and connections.
MySQL pre-allocate memory for each connections and de-allocate only when the connection get closed. When new connections are querying, system should have enough resources such memory, network and computation power to satisfy the user requests.
Also, you should consider increasing the open tables limit in MySQL server to accommodate the additional request. And finally. it is very important to close the connections which are completed transaction on the server.
Error 1040 Too many connections — ошибка, которая возникает при превышении максимального количества возможных подключений к серверу баз данных со стороны скриптов сайта.
Устраняется, как правило, увеличением лимита в конфигурации сервера.
Обычно превышением количества соединений проявляется как прекративший работать сайт. Ошибку можно увидеть попробовав подключиться к базе данных с реквизитами пользователя, от имени которого работает сайт.
mysql -u USERNAME -p
Enter password:
ERROR 1040 (08004): Too many connections
От имени суперпользователя подключиться удастся в случае если сайт работает не от root.
mysql -u root -p
Лимит существует для пользователя, если сайт работает от root (что именно из-за этого является плохой практикой) и появилась такая ошибка — требуется перезапуск службы MySQL через systemctl restart mysql.
Если удалось зайти в консоль MySQL проверяем актуальное значение директивы max_user_connection. В данном случае нас интересует прежде всего оно.
show status like ‘%connected%’;
+-------------------+-------+ | Variable_name | Value | +-------------------+-------+ | Threads_connected | 151 | +-------------------+-------+ 1 row in set (0.01 sec)
А также действующий лимит
show global variables like ‘%connections%’;
+----------------------+-------+ | Variable_name | Value | +----------------------+-------+ | max_connections | 151 | | max_user_connections | 0 | +----------------------+-------+ 2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
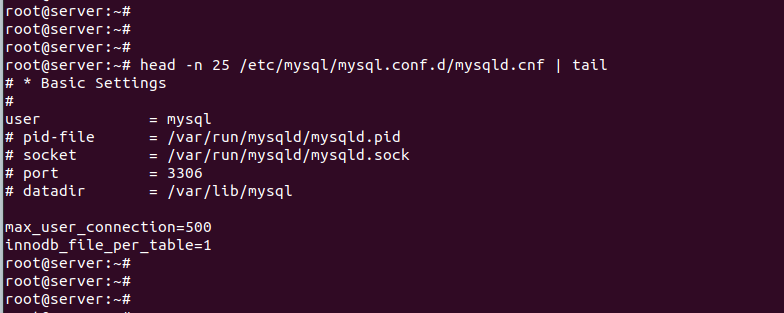
Лимит достигнут, скрипты при этом продолжают делать запросы. Исправить ситуацию можно добавив в /etc/mysql/my.cnf такую строку
max_user_connection=500
Параметр может задавать не только в /etc/mysql/my.cnf, но и в любом файле, который подключается в /etc/mysql/my.cnf. Главное блок, в который добавляются настройки, он должен определяться директивой [mysqld].
Пример приведен на скриншоте
Затем перезапустив MySQL
systemctl restart mysql
Без перезапуска того же результата можно добиться установив новое значение глобальной переменной, от имени root в консоли MySQL это делается таким образом:
set global max_connections = 500;
Значение будет в силе пока работает процесс MySQL — до следующего перезапуска. Установку глобальной переменной в консоли можно использовать как временное решение. На постоянно изменить значение можно только в конфигурационном файле с последующим перезапуском службы.
Лимит теперь увеличен и сайт должен вновь стать доступен.
Часто причиной является большая активность аудитории и длительные запросы на изменение данных. Они протекают с блокировками, если используются таблицы типа MyISAM получить значительное улучшение можно конвертировав их в InnoDB.
Читайте также про оптимизацию настроек MySQL.
Over the years of being a DBA, I had to deal with all kinds of problems in the database. One of the most common problems I faced is the one related to the well-known error “ERROR 1040 (08004): Too many connections”. A lot has been written about this error. Still, the users keep falling into this trap, maybe because of a poorly configured database, a change in the application components, or just because of a sudden increase of connections in the application. At some point, we all face this issue in our careers, not only once but many times. The main objective of this blog post is to point out the new administrative connections allowed on MySQL 8, as these connections can save us from restarting the instance in case this happens.
Default behavior
We know that the amount of connections allowed in the database is defined by the parameter “max_connections.” The default value for this parameter is 151, and it can be changed dynamically, which means without a database restart. If the connections in the database are maxed out, we will hit the dreadful message “ERROR 1040 (08004): Too many connections”. It is important to remember that out of the box, MySQL allows one extra connection, this connection is reserved for the users with “SUPER” privilege (already deprecated here) or the CONNECTION_ADMIN privilege.
I’ll show an example of this feature; for this example, I have an instance with “max_connections=20”, and I have three users, user “monitor1” has only the PROCESS privilege, user “admin1” has the privileges PROCESS and CONNECTION_ADMIN, finally user “admin2” has the privilege SUPER (deprecated). We will see how MySQL treats these connections in the event of having an instance maxed out on user connections:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 |
— execute all 20 concurrent connections sysbench oltp_read_write —table—size=1000000 —db—driver=mysql —mysql—host=localhost —mysql—db=sbtest —mysql—user=root —mysql—password=«***» —num—threads=20 —time=0 —report—interval=1 run — test with user monitor1 [root@rocky—test1 ~]# mysql -u monitor1 -p Enter password: ERROR 1040 (08004): Too many connections — test with user admin1 [root@rocky—test1 ~]# mysql -u admin1 -p Enter password: Welcome to the MySQL monitor. Commands end with ; or g. Your MySQL connection id is 144 Server version: 8.0.29—21 Percona Server (GPL), Release 21, Revision c59f87d2854 Copyright (c) 2009—2022 Percona LLC and/or its affiliates Copyright (c) 2000, 2022, Oracle and/or its affiliates. Oracle is a registered trademark of Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates. Other names may be trademarks of their respective owners. Type ‘help;’ or ‘h’ for help. Type ‘c’ to clear the current input statement. mysql> show grants; +————————————————————————+ | Grants for admin1@% | +————————————————————————+ | GRANT PROCESS ON *.* TO `admin1`@`%` | | GRANT CONNECTION_ADMIN ON *.* TO `admin1`@`%` | +————————————————————————+ 2 rows in set (0.00 sec) mysql> select count(1) from information_schema.processlist; +—————+ | count(1) | +—————+ | 22 | +—————+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec) — test with user admin2 [root@rocky—test1 ~]# mysql -u admin2 -p Enter password: Welcome to the MySQL monitor. Commands end with ; or g. Your MySQL connection id is 145 Server version: 8.0.29—21 Percona Server (GPL), Release 21, Revision c59f87d2854 Copyright (c) 2009—2022 Percona LLC and/or its affiliates Copyright (c) 2000, 2022, Oracle and/or its affiliates. Oracle is a registered trademark of Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates. Other names may be trademarks of their respective owners. Type ‘help;’ or ‘h’ for help. Type ‘c’ to clear the current input statement. mysql> show grants; +——————————————————+ | Grants for admin2@% | +——————————————————+ | GRANT SUPER ON *.* TO `admin2`@`%` | +——————————————————+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec) mysql> select count(1) from information_schema.processlist; +—————+ | count(1) | +—————+ | 1 | +—————+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec) |
As you can see, one single connection with a user with “CONNECTION_ADMIN” or “SUPER” privilege is allowed, however, when user “monitor1” tried to connect, it was not possible because it did not have any of those privileges. Once we gain access to the database, we can easily increase the connections by changing the variable “max_connections” online and then checking the origin of the problem. It is important to remember that only one of these connections is allowed, so please don’t grant these privileges to any user, or you could still be locked out of your database.
|
– trying a second connection with user admin1 [root@rocky—test1 ~]# mysql -u admin1 -p Enter password: ERROR 1040 (HY000): Too many connections |
Usually, when this problem occurs, and we cannot gain access to MySQL, the immediate solution is to restart the database and deal with all consequences that this causes, but hey… that is better than rejecting connections for several minutes during the business’s normal operating hours. There is another alternative to gain access to the database, which is by using GDB, but it is not always possible, and Too many connections? No problem! is an article we wrote about this tool in the past, the article is a bit old but still valid.
Side note for Percona Server for MySQL and MariaDB
Percona Server for MySQL, in versions before 8.0.14, had another way to access the database instance, similar to the new feature introduced in version 8.0.14. It was by enabling variables “extra_port” and “extra_max_connections,” and the usage of these variables is out of the scope of this blog post, but the objective of such variables was to allow connections to the database even when the database maximum connections have been reached. Remember that those variables were removed on version 8.0.14, and if found in the config file, the instance will not start, and an error will be shown. Like Percona Server for MySQL, MariaDB had a similar implementation for the same variables. Documentation for MariaDB can be found here.
New feature
Starting with MySQL 8.0.14, a new “Administrative Connections” or “Administrative Network Interface” feature was introduced. This feature allows connections to the database through an administrative port, there is no limit on the number of administrative connections. The difference between this feature and the single connection shown in the previous example is that this is a different port, and it does not limit the connections to only one but more than one connection if required. This should allow us to access the database when the user connections are maxed out and work from there to increase the connections or kill some of the application connections.
The easiest way to enable the “Administrative Connections” is to define the “admin_address” variable, this is the IP address that the administrative connections will listen to, for example, if you only want to allow local connections, you can define this variable as “127.0.0.1”, or if you want to connect through the network, you can define this variable as the server’s IP address. This variable is not dynamic, which means it will require a database restart. By default, this variable is empty, meaning the administrative interface is disabled. Another related variable is “admin_port”; this variable defines the port MySQL will listen to for the administrative connections, the default value for this variable is 33062. Once you define both variables and restart the database, you will see a message indicating the admin interface is ready for connections in the error log:
|
2023—02—28T14:42:44.383663Z 0 [System] [MY—013292] [Server] Admin interface ready for connections, address: ‘127.0.0.1’ port: 33062 |
Now that the admin interface is configured, you need to define the users that can access this administrative connection. These users will require the “SERVICE_CONNECTION_ADMIN” privilege; otherwise, they won’t be able to connect to it. Following our initial example, I have granted the “SERVICE_CONNECTION_ADMIN” to the user “admin1” but not to user “admin2”
|
mysql> show grants for admin1; +————————————————————————————————————+ | Grants for admin1@% | +————————————————————————————————————+ | GRANT PROCESS ON *.* TO `admin1`@`%` | | GRANT CONNECTION_ADMIN,SERVICE_CONNECTION_ADMIN ON *.* TO `admin1`@`%` | +————————————————————————————————————+ 2 rows in set (0.00 sec) mysql> show grants for admin2; +——————————————————+ | Grants for admin2@% | +——————————————————+ | GRANT SUPER ON *.* TO `admin2`@`%` | +——————————————————+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec) |
Testing connection to the admin interface, we see that only user “admin1” is allowed, while user “admin2” connection is rejected for lacking privilege “SERVICE_CONNECTION_ADMIN.” Also, we can confirm user “admin1” is connected to port 33062, which is the port used for the admin interface.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 |
— testing user admin1 [root@rocky—test1 ~]# mysql -h 127.0.0.1 -P 33062 -u admin1 -p Enter password: Welcome to the MySQL monitor. Commands end with ; or g. Your MySQL connection id is 23 Server version: 8.0.29—21 Percona Server (GPL), Release 21, Revision c59f87d2854 Copyright (c) 2009—2022 Percona LLC and/or its affiliates Copyright (c) 2000, 2022, Oracle and/or its affiliates. Oracle is a registered trademark of Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates. Other names may be trademarks of their respective owners. Type ‘help;’ or ‘h’ for help. Type ‘c’ to clear the current input statement. mysql> s ——————— mysql Ver 8.0.29—21 for Linux on x86_64 (Percona Server (GPL), Release 21, Revision c59f87d2854) Connection id: 23 Current database: Current user: admin1@localhost SSL: Cipher in use is TLS_AES_256_GCM_SHA384 Current pager: stdout Using outfile: » Using delimiter: ; Server version: 8.0.29—21 Percona Server (GPL), Release 21, Revision c59f87d2854 Protocol version: 10 Connection: 127.0.0.1 via TCP/IP Server characterset: utf8mb4 Db characterset: utf8mb4 Client characterset: utf8mb4 Conn. characterset: utf8mb4 <strong>TCP port: 33062</strong> Binary data as: Hexadecimal Uptime: 50 min 27 sec Threads: 3 Questions: 188 Slow queries: 0 Opens: 335 Flush tables: 3 Open tables: 269 Queries per second avg: 0.062 ——————— — testing user admin2 [root@rocky—test1 ~]# mysql -h 127.0.0.1 -P 33062 -u admin2 -p Enter password: <strong>ERROR 1227 (42000): Access denied; you need (at least one of) the SERVICE_CONNECTION_ADMIN privilege(s) for this operation</strong> |
Conclusion
If you are using MySQL 8.0.14 or higher, you should enable the admin interface, as we have seen, enabling this feature is super easy and leverages a great feature by allowing access to the database to DBAs in case of an event of “ERROR 1040 (08004): Too many connections”. This new feature does not affect normal database performance and brings great power to DBAs. Please consider adding the privilege “SERVICE_CONNECTION_ADMIN” only to administrative users, not application users, the idea is not to abuse this feature. If you are still using a lower version of Percona Server for MySQL, please remember you can configure variables “extra_port” and “extra_max_connections” to access your database in case you face a max connections issue.
Percona Distribution for MySQL is the most complete, stable, scalable, and secure open-source MySQL solution available, delivering enterprise-grade database environments for your most critical business applications… and it’s free to use!
Try Percona Distribution for MySQL today!
If you have encountered the error “Too many connections” while trying to connect to a MySQL Server, that means it reached the maximum number of connections, or all available permitted are in use by other clients and your connection attempts will get rejected.
That number of connections is defined via the max_connections system variable. To open for more connections, you can set a higher value for max_connections.
To see the current value of max_connections, run this command:
SHOW VARIABLES LIKE "max_connections";
By default, it’s set to 151. But MySQL actually allows up to max_connections + 1, which is 151 + 1 for the default setting. The extra connection can be used by the user with SUPER privilege only.
To increase the max_connections value, let’s say 500, run this command:
SET GLOBAL max_connections = 500;
The command takes effect right after you execute it, but it only applies to the current session. If you want it to be permanent until you re-adjust it the next time, you have to edit the configuration file my.cnf (normally it’s stored in /etc/my.cnf).
Under the [mysqld] section add the following line:
Then restart the MySQL server to take effect.
One thing to keep in mind that there is no hard limit to setting up maximum max_connections value, but increasing it will require more RAM to run. The number of maximum connections permitted has to be calculated based on how much RAM you have and how much is used per connection. In many cases, if you run out of usable disc space on your server partition or drive, MySQL might also return this error.
The maximum number can be estimated by the formula:
max.connection=(available RAM-global buffers)/thread buffers
So increase it with caution.
Need a good GUI Tool for MySQL? TablePlus is a modern, native tool with an elegant UI that allows you to simultaneously manage multiple databases such as MySQL, PostgreSQL, SQLite, Microsoft SQL Server and more.
Download TablePlus for Mac. It’s free anyway!
Not on Mac? Download TablePlus for Windows.
On Linux? Download TablePlus for Linux
Need a quick edit on the go? Download TablePlus for iOS.