Добрый вечер.
Хотелось бы узнать, как избавиться от данной ошибки.
itemDesc.replace(';', '')
В этой строке возникает ошибка, в данной переменной находится html код.
Происходит ошибка:
TypeError: ‘NoneType’ object is not callable
- python
angry
8,64717 золотых знаков73 серебряных знака180 бронзовых знаков
задан 6 окт 2011 в 14:01
xenollxenoll
4012 золотых знака7 серебряных знаков20 бронзовых знаков
2 ответа
ответ дан 6 окт 2011 в 16:28
KanviKanvi
1561 серебряный знак5 бронзовых знаков
Уже разобрался, понимал, что нужно переменную объявить строкой, но вот такой вариант почему-то не работал
itemDesc = str(itemDesc)
Подсказали вот так:
itemDesc = itemDesc.__str__().replace('', '')<br>
Заработало.
angry
8,64717 золотых знаков73 серебряных знака180 бронзовых знаков
ответ дан 6 окт 2011 в 19:32
xenollxenoll
4012 золотых знака7 серебряных знаков20 бронзовых знаков
You will encounter the TypeError: ‘NoneType’ object is not callable if you try to call an object with a None value like a function. Only functions respond to function calls.
In this tutorial, we will look at examples of code that raise the TypeError and how to solve it.
Table of contents
- TypeError: ‘nonetype’ object is not callable
- Example #1: Printing Contents From a File
- Solution
- Example #2: Calling a Function Within a Function
- Solution
- Summary
TypeError: ‘nonetype’ object is not callable
Calling a function means the Python interpreter executes the code inside the function. In Python, we can only call functions. We can call functions by specifying the name of the function we want to use followed by a set of parentheses, for example, function_name(). Let’s look at an example of a working function that returns a string.
# Declare function
def simple_function():
print("Hello World!")
# Call function
simple_function()
Hello World!
We declare a function called simple_function in the code, which prints a string. We can then call the function, and the Python interpreter executes the code inside simple_function().
None, string, tuple, or dictionary types do not respond to a function call because they are not functions. If you try to call a None value, the Python interpreter will raise the TypeError: ‘nonetype’ object is not callable.
Let’s look at examples of raising the error and how to solve them.
Example #1: Printing Contents From a File
Let’s look at an example of a program that reads a text file containing the names of famous people and prints the names out line by line.
The text file is called celeb_names.txt and contains the following names:
Leonardo DiCaprio Michael Jordan Franz Kafka Mahatma Gandhi Albert Einstein
The program declares a function that reads the file with the celebrity names.
# Declare function
def names():
with open("celeb_names.txt", "r") as f:
celebs = f.readlines()
return celebs
The function opens the celeb_names.txt file in read-mode and reads the file’s contents into the celebs variable. We will initialize a variable to assign the celebrity names.
# Initialize variable names = None
We can then call our get_names() function to get the celebrity names then use a for loop to print each name to the console.
# Call function
names = names()
# For loop to print out names
for name in names:
print(name)
Let’s see what happens when we try to run the code:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------- TypeError Traceback (most recent call last) 1 names = names() TypeError: 'NoneType' object is not callable
Unfortunately, we raise the NoneType object is not callable. This error occurs because we declared both a function and a variable with the same name. We declared the function first then the variable declaration overrides the function declaration. Any successive lines of code referring to names will refer to the variable, not the function.
Solution
We can either rename the function or the variable to solve this error. Adding a descriptive verb to a function name is a good way to differentiate from a variable name. Let’s change the function name from names() to get_names().
# Declare function with updated name
def get_names():
with open("celeb_names.txt", "r") as f:
celebs = f.readlines()
return celebs
# Initialize variable with None
names = None
# Call function and store values in names variable
names = get_names()
# Loop over all names and print out
for name in names:
print(name)
Renaming the function name means we will not override it when declaring the names variable. We can now run the code and see what happens.
Leonardo DiCaprio Michael Jordan Franz Kafka Mahatma Gandhi Albert Einstein
The code successfully works and prints out all of the celebrity names.
Alternatively, we could remove the initialization, as it is not required in Python. Let’s look at the revised code:
# Declare function with updated name
def get_names():
with open("celeb_names.txt", "r") as f:
celebs = f.readlines()
return celebs
# Call function and store values in names variable without initializing
names = get_names()
# Loop over all names and print out
for name in names:
print(name)
Leonardo DiCaprio Michael Jordan Franz Kafka Mahatma Gandhi Albert Einstein
Example #2: Calling a Function Within a Function
Let’s look at an example of two functions; one function executes a print statement, and the second function repeats the call to the first function n times.
def hello_world():
print("Hello World!")
def recursive(func, n): # Repeat func n times
if n == 0:
return
else:
func()
recursive(func, n-1)
Let’s see what happens when we try to pass the call to the function hello_world() to the recursive() function.
recursive(hello_world(), 5)
TypeError Traceback (most recent call last)
1 recursive(hello_world(), 5)
3 return
4 else:
5 func()
6 recursive(func, n-1)
7
TypeError: 'NoneType' object is not callable
Solution
To solve this error, we need to pass the function object to the recursive() function, not the result of a call to hello_world(), which is None since hello_world() does not return anything. Let’s look at the corrected example:
recursive(hello_world, 5)
Let’s run the code to see the result:
Hello World! Hello World! Hello World! Hello World! Hello World!
Summary
Congratulations on reading to the end of this tutorial. To summarize, TypeError’ nonetype’ object is not callable occurs when you try to call a None type value as if it were a function. TypeErrors happen when you attempt to perform an illegal operation for a specific data type. To solve this error, keep variable and function names distinct. If you are calling a function within a function, make sure you pass the function object and not the result of the function if it returns None.
For further reading on not callable TypeErrors, go to the articles:
- How to Solve Python TypeError: ‘tuple’ object is not callable.
- How to Solve Python TypeError: ‘bool’ object is not callable.
- How to Solve Python TypeError: ‘_io.TextIOWrapper’ object is not callable.
To learn more about Python, specifically for data science and machine learning, go to the online courses page on Python.
Have fun and happy researching!
“TypeError: ‘NoneType’ object is not callable” is a common python error that shows up in many ways. What is the cause of it and how to solve it? Let’s follow our article, and we will help you.
What is the cause of this error?
When you attempt to call an object with a None value, such as a function, you will get the TypeError: “NoneType” object is not callable error message. Function calls only have responses from functions.
Example code 1: Attribute and Method have the same name
class Student:
def __init__(obj):
obj.fullname = None
def fullname(obj):
return obj.fullname # Same name with the method
def printMsg():
print('Welcome to LearnShareIT')
def msgStudent(name, function):
print("Hi", name)
function()
exStudent = Student()
exStudent.fullname() # TypeError: 'NoneType' object is not callable
Error Message
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
TypeError Traceback (most recent call last)
<ipython-input-4-65eab4cbbd19> in <module>
14
15 exStudent = Student()
---> 16 exStudent.fullname()
TypeError: 'NoneType' object is not callableExample code 2: Misunderstand when calling a function
class Student:
def __init__(obj):
obj.fullname = None
def getFullName(obj):
return obj.fullname
def printMsg():
print('Welcome to LearnShareIT')
def msgStudent(name, function):
print("Hi", name)
function() # Calling None object as a function
exStudent = Student()
exStudent.fullname = "Robert Collier"
msgStudent(exStudent.getFullName(), printMsg()) # TypeError: 'NoneType' object is not callable
Error Message
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
TypeError Traceback (most recent call last)
<ipython-input-16-618076368e04> in <module>
16 exStudent.fullname = "Robert Collier"
17
---> 18 msgStudent(exStudent.getFullName(), printMsg())
<ipython-input-16-618076368e04> in msgStudent(name, function)
11 def msgStudent(name, function):
12 print("Hi",name)
---> 13 function() # Calling None object as a function
14
15 exStudent = Student()
TypeError: 'NoneType' object is not callableTo solve this error, let’s follow two solutions we suggest below:
1) Change the name of method in class
The reason of this error is that when you name the function as the name of a attribute, the attribute will be the first priority to access. As a result, you call the attribute as a function, which cause the Error as the example.
You can change the method name: fullname(obj) to getFullName(obj) as shown the code in the below example to fix the error.
Code sample
class Student:
def __init__(obj):
obj.fullname = None
def getFullName(obj):
return obj.fullname
exStudent = Student()
exStudent.fullname = "Robert Collier"
print(exStudent.getFullName())
Output
'Robert Collier'2) Remove the parentheses ‘()’
When you pass a non-returning function as a parameter of another function, it is a common mistake to add the parenthesis after the function’s name. It means you call the result of the function as a function accidentally.
Remove the parentheses ‘()’ in the msgStudent(exStudent.getFullName(), printMsg()) statement. The alternative statement would be msgStudent(exStudent.getFullName(), printMsg). When you do that, your error will be fixed.
Code sample
class Student:
def __init__(obj):
obj.fullname = None
def getFullName(obj):
return obj.fullname
def printMsg():
print('Welcome to LearnShareIT')
def msgStudent(name, function):
print("Hi", name)
function() # Calling None object as a function
exStudent = Student()
exStudent.fullname = "Robert Collier"
msgStudent(exStudent.getFullName(), printMsg) # Remove ... ()
Output:
Hi Robert Collier
Welcome to LearnShareITSummary
In conclusion, “TypeError: ‘nonetype’ object is not callable” occurs when you call a None object as a function. The only way to solve the problem is understanding which parameter is an object and which parameter is a function.
Maybe you are interested:
- TypeError: ‘NoneType’ object is not iterable in Python
- TypeError: ‘set’ object is not subscriptable in Python
- TypeError: ‘str’ object does not support item assignment
- TypeError: a bytes-like object is required, not ‘str’ in python

My name is Robert Collier. I graduated in IT at HUST university. My interest is learning programming languages; my strengths are Python, C, C++, and Machine Learning/Deep Learning/NLP. I will share all the knowledge I have through my articles. Hope you like them.
Name of the university: HUST
Major: IT
Programming Languages: Python, C, C++, Machine Learning/Deep Learning/NLP
In Python, a specific data type referred to as “NoneType” is used to store “None” value. Python uses the keyword “None” to store the “Null/None” value in a variable. Some functions in Python also return the “None” value, such as the sort() function.
While dealing with a “None” value, “TypeError: NoneType object is not callable” may occur in Python. To resolve this error, various solutions are provided by Python.
This blog will provide a comprehensive guide on resolving the “TypeError: NoneType object is not callable” in Python. This guide contains the following contents:
- Reason 1: Using the Same Name for Function and Variable
- Solution: Rename Variable or Function
- Reason 2: Class Methods and Class Properties Have the Same Name
- Solution: Rename the Class Method or Class Attributes
- Reason 3: Calling None Variable as a Function
- Solution: Removing Parentheses
So, let’s get started!
Reason 1: Using the Same Name for Function and Variable
This “TypeError” occurs when we try to use the same name for a function and variable in a Python program. Here is an example:
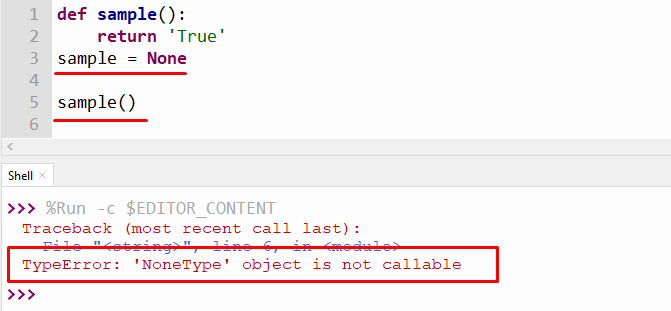
The above output shows the “TypeError” because the function “sample” and variable “sample” are initialized with the same name in a program.
Solution: Rename Variable or Function
To fix this error, make sure to rename the function or variable in a program. After renaming the function or variable, re-execute the program to remove the error.
Code:
def sample1():
return 'True'
sample = None
print(sample1())
In the above code, the user-defined function is renamed from “sample” into “sample1”. After renaming the function name, the function value will be accessed using parentheses.
Output:
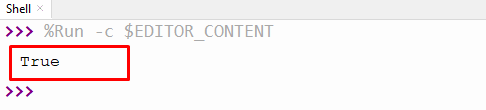
The above output verified that the function returns a “None” value.
Reason 2: Class Methods and Class Properties Have the Same Name
The other prominent reason which produces this error in the program is when the user uses the same name for the class property and class method. Here is an example:
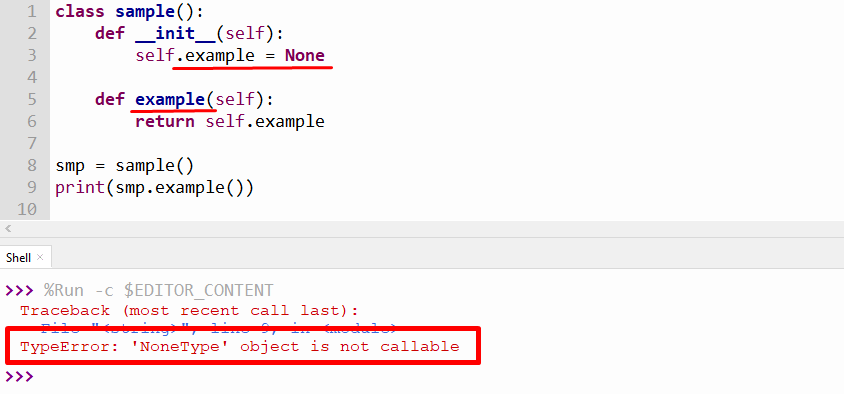
The above output, the class method “example”, and the class property/attribute “self.example” have the same name in a program.
Solution: Rename the Class Method or Class Attributes
To rectify this error, rename the method of the class and re-execute the Python script. Here’s an example:
Code:
class sample():
def __init__(self):
self.example = None
def value(self):
return "True"
smp = sample()
print(smp.value())
In the above code, the class method name “example” is renamed to “value”. After renaming the method, the program runs successfully without any errors.
Output:
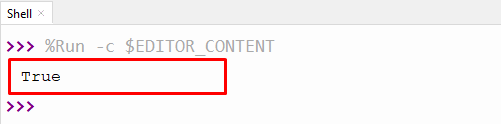
The above output verified that the class method executes the program successfully.
Reason 3: Calling None Variable as a Function
The error also arises when the user calls the none value as if it were a function in a Python program. Below is an example of this error:
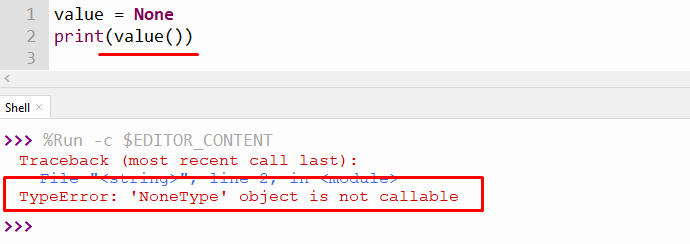
The above output displays the “TypeError” because the none value variable is called as a function in Python.
Solution: Removing Parentheses
To resolve this error, you need to remove the parentheses or correct the assignment. Let’s look at the below solutions code:
Code:
value = None print(value)
In the above code, the “None” value is assigned to the variable “value” in the program. The value is displayed on the screen using the “print()” function.
Output:
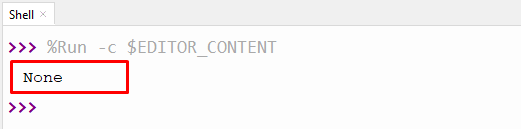
This output displays the value of the variable “value“.
Conclusion
The “TypeError: NoneType object is not callable” arises in Python when we try to access a “None” variable as a Function or use the same name for a variable and function, etc. To resolve this error, various solutions are provided, such as renaming functions or variables, renaming class methods, and removing parentheses while accessing variables. This Python article has presented a detailed guide on resolving the “NoneType object is not callable” error using appropriate examples.
In Python to call a function, we use the function name followed by the parenthesis
()
. But if we try to call other Python objects like,
int
,
list
,
str
,
tuple
, etc., using parenthesis, we receive the TypeError Exception with an error message that the following object is not callable.
None
is a reserved keyword value in Python, which data type is
NoneType
. If we put parenthesis »
()
» after a None value and try to call it as a function we receive the
TypeError: 'NoneType' object is not callable
Error.
In this Python guide, we will walk through this Python error and discuss why it occurs in Python and how to solve it. We will also discuss a common example scenario where many Python learners commit mistakes while writing the program and encounter this error.
So let’s get started with the Error Statement!
The
TypeError: 'NoneType' object is not callable
is a standard Python error statement and like other error statements, it can be divided into two parts.
-
Exception Type
TypeError
-
Error Message (
'NoneType' object is not callable
)
1. TypeError
TypeError is a standard Python exception, it occurs in a Python program when we perform an unsupportable operation on a specific Python object. For instance, integer objects do not support indexing in Python. And if we try to perform indexing on an integer object, we also receive the
TypeError
with some error message.
2. ‘NoneType’ object is not callable
«NoneType object is not callable» is an error message, and it is raised in the program when we try to call a NoneType object as a function. There is only one NoneType object value in Python
None
# None Value
obj = None
print('Type of obj is: ',type(obj))
Output
Type of obj is: <class 'NoneType'>And if we try to call the None value objects or variables as a function using parenthesis () we receive the TypeError with the message ‘NoneType’ object is not callable’
Example
# None Value
obj = None
# call None obj as a function
obj()
Output
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "main.py", line 5, in
obj()
TypeError: 'NoneType' object is not callable
In this example, we tried to call the
obj
variable as a function
obj()
and we received the Error. The value of
obj
is
None
which make the
obj
a
NoneType
object, and we can not perform function calling on a NoneType object. When the Python interpreter read the statement
obj()
, it tried to call the obj as a function, but soon it realised that
obj
is not a function and the interpreter threw the error.
Common Example Scenario
The most common example where many Python learners encounter this error is when they use the same name for a function and a None Type variable. None value is mostly used to define an initial value, and if we define a function as the same name of the variable with None value we will receive this error in our Program.
Example
Let’s create a Python function
result()
that accepts a list of paired tuples
students [(name,marks)]
and return the name and the marks of the student who get the maximum marks.
def result(students):
# initilize the highest_marks
highest_marks = 0
for name, marks in students:
if marks> highest_marks:
rank1_name = name
highest_marks =marks
return (rank1_name, highest_marks)
students = [("Aditi Musunur", 973),
("Amrish Ilyas", 963),
("Aprativirya Seshan", 900),
("Debasis Sundhararajan", 904),
("Dhritiman Salim",978) ]
# initial result value
result = None
# call the result function
result = result(students)
print(f"The Rank 1 Student is {result[0]} with {result[1]} marks")
Output
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "main.py", line 22, in
result = result(students)
TypeError: 'NoneType' object is not callable
Break the code
In this example, we are getting the error in 22 with
result = result(students)
statement. This is because at that point result is not a function name but a
None
value variable. Just above the function calling statement, we have defined the
result
value as None using the
result = None
statement.
As Python executes its code from top to bottom the value of the
result
object changed from
function
to
None
when we define the
result
initial value after the function definition. And the Python interpreter calls the None object as a function when it interprets the
result()
statement.
Solution
The solution to the above problem is straightforward. When writing a Python program we should always consider using the different names for functions and value identifiers or variables. To solve the above problem all we need to do is define a different name for the result variable that we used to store the return value of the result function.
def result(students):
# initilize the highest_marks
highest_marks = 0
for name, marks in students:
if marks> highest_marks:
rank1_name = name
highest_marks =marks
return (rank1_name, highest_marks)
students = [("Aditi Musunur", 973),
("Amrish Ilyas", 963),
("Aprativirya Seshan", 900),
("Debasis Sundhararajan", 904),
("Dhritiman Salim",978) ]
# initialize the initial value
rank1= None
# call the result function
rank1 = result(students)
print(f"The Rank 1 Student is {rank1[0]} with {rank1[1]} marks")
Output
The Rank 1 Student is Dhritiman Salim with 978 marks
Conclusion
In this Python error tutorial, we discussed
TypeError: 'NoneType' object is not callable
Error, and learn why this error occurs in Python and how to debug it. You will only encounter this error in your Python program when you try to call a None object as a function. To debug this error you carefully need to read the error and go through the code again and look for the line which is causing this error.
With some practice, you will be able to solve this error in your program in no time. If you are still getting this error in your Python program, you can share the code in the comment section. We will try to help you in debugging.
People are also reading:
-
Python Subdomain Scanner
-
WiFi Scanner in Python
-
How to create Logs in Python?
-
Python Data Structure
-
Best Way to Learn Python
-
Python vs PHP
-
Best Python Books
-
Best Python Interpreters
-
Python Multiple Inheritance
-
Class and Objects in Python
