This is my Code
public class Workshop3
{
public static void main (String [] args)
{
System.out.println ("please enter radius of circle");
double radius;
Scanner keyboard = new Scanner (System.in);
keyboard.nextDouble (radius);
}
}
The error I recieve is
cannot find symbol — class scanner
on the line
Scanner keyboard = new Scanner (System.in);
gunr2171
15.9k25 gold badges61 silver badges87 bronze badges
asked May 11, 2011 at 3:56
0
As the OP is a new beginner to programming, I would like to explain more.
You wil need this line on the top of your code in order to compile:
import java.util.Scanner;
This kind of import statement is very important. They tell the compile of which kind of Scanner you are about to use, because the Scanner here is undefined by anyone.
After a import statement, you can use the class Scanner directly and the compiler will know about it.
Also, you can do this without using the import statement, although I don’t recommend:
java.util.Scanner scanner = new java.util.Scanner(System.in);
In this case, you just directly tell the compiler about which Scanner you mean to use.
answered May 11, 2011 at 4:08
lamwaiman1988lamwaiman1988
3,71715 gold badges55 silver badges87 bronze badges
0
You have to import java.util.Scanner at first line in the code
import java.util.Scanner;
answered May 11, 2011 at 4:00
![]()
Eng.FouadEng.Fouad
115k70 gold badges312 silver badges416 bronze badges
0
You need to include the line import java.util.Scanner; in your source file somewhere, preferably at the top.
![]()
answered May 11, 2011 at 3:58
dlevdlev
48k5 gold badges125 silver badges132 bronze badges
You can resolve this error by importing the java.util.* package — you can do this by adding following line of code to top of your program (with your other import statements):
import java.util.*;
![]()
answered Jul 15, 2016 at 9:25
sometimes this can occur during when we try to print string from the user so before we print we have to use
eg:
Scanner scan=new Scanner (System.in);
scan.nextLine();
// if we have output before this string from the user like integer or other dat type in the buffer there is /n (new line) which skip our string so we use this line to print our string
String s=scan.nextLine();
System.out.println(s);
answered May 7, 2020 at 18:01
Please add the following line on top of your code
*import java.util.*;*
This should resolve the issue
![]()
Jim Simson
2,7643 gold badges22 silver badges30 bronze badges
answered Sep 5, 2020 at 12:58
Add import java.util.Scanner; at the very top of your code. Worked for me.
answered Dec 15, 2020 at 18:51
![]()
Возможно ошибка
com/javarush/task/task03/task0318/Solution.java:12: error: cannot find symbol
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
^
symbol: class Scanner
location: class com.javarush.task.task03.task0318.Solution
com/javarush/task/task03/task0318/Solution.java:12: error: cannot find symbol
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
^
symbol: class Scanner
location: class com.javarush.task.task03.task0318.Solution
Вот ошибка которую выдаёт компилятор.Подскажите какой import нужно добавить что бы компилятор мог закомпилировать или может у меня тут ошибка буду рад если исправите меня
package com.javarush.task.task03.task0318;
/*
План по захвату мира
*/
import java.io.*;
public class Solution {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
String name = scanner.nextLine();
int age = scanner.nextInt();
System.out.println(name + «захватим мир через » + age+ » лет. Му-ха-ха!»);
}
}
Этот веб-сайт использует данные cookie, чтобы настроить персонально под вас работу сервиса. Используя веб-сайт, вы даете согласие на применение данных cookie. Больше подробностей — в нашем Пользовательском соглашении.
What is the Cannot Find Symbol Java Error?
Learn via video course

Java Course — Mastering the Fundamentals
Tarun Luthra
Free
5
Enrolled: 54029
Start Learning
The Cannot Find Symbol in Java is a compilation error that occurs when we try to refer to something that is not present in the Java Symbol Table. A very common example of this error is using a variable that is not declared in the program.
Java compilers create and maintain Symbol tables. The symbol table stores the information of the identifiers i.e. classes, interfaces, variables, and methods in the given source of code. When we use these identifiers in our code, the compiler looks up to the symbol table for information. If the identifier is not declared or is not present in the given scope the compiler throws ‘Cannot Find Symbol’.
What Causes the Java Cannot Find Symbol Error?
There are multiple ways and reasons this error can occur, they all boil down to the fact that the online Java compiler couldn’t find the identifier in the Symbol table. Some of the very commonly made mistakes are listed below:
- Java is case sensitive, thus hello and Hello are two different variables.
- If identifiers are misspelled say the variable’s name is name and we are trying to access nmae can cause an error.
- Sometimes variables are declared in a particular iterating loop or method and if we try to call them from outside causes an error as it is out of the scope of the variable.
- Using variables without their declaration is also the common cause of the Java ‘Cannot find Symbol’ error.
- Sometimes we use methods from classes of a different package. To do so we are required to import the package of the class. Missing import statements can cause the error too.
- Use of underscore, dollar sign, numbers, letter even a character before or after different from the initial declaration can cause ‘Cannot Find Symbol’.
Examples of Java Cannot Find Symbol error
Let us now see these common errors in the form of code:
Example 1
Let us take a very simple example of a function that takes user input of a number and returns if the number is even or odd.
Output:
In the example above, the Scanner class is not imported and thus it is throwing a Cannot Find Symbol error. The compiler is not able to find Scanner in the program. Once we import the package, it is able to identify the Scanner class.
Example 2
Another example is wrong spelling and undeclared variables. Let us take a simple example where we multiply a variable a few times in a loop.
Output:
In the example above we can see 3 errors, all of them being ‘cannot find symbol’. The first one is because N is not declared in the program, and the two are because we declared finalResult but we are calling final_Result. Thus, a single underscore can also cause an error.
Example 3
Lastly, out-of-scope variables also cause a ‘Cannot find Symbol’ error, below example demonstrates it.
Output:
In the example above, the sum variable is declared inside the for loop and its scope is only inside for loop. As we are trying to access it outside the for loop, it is causing the error.
Structure of Java Cannot Find Symbol
Look at the output generated by the compiler for the 3rd example:
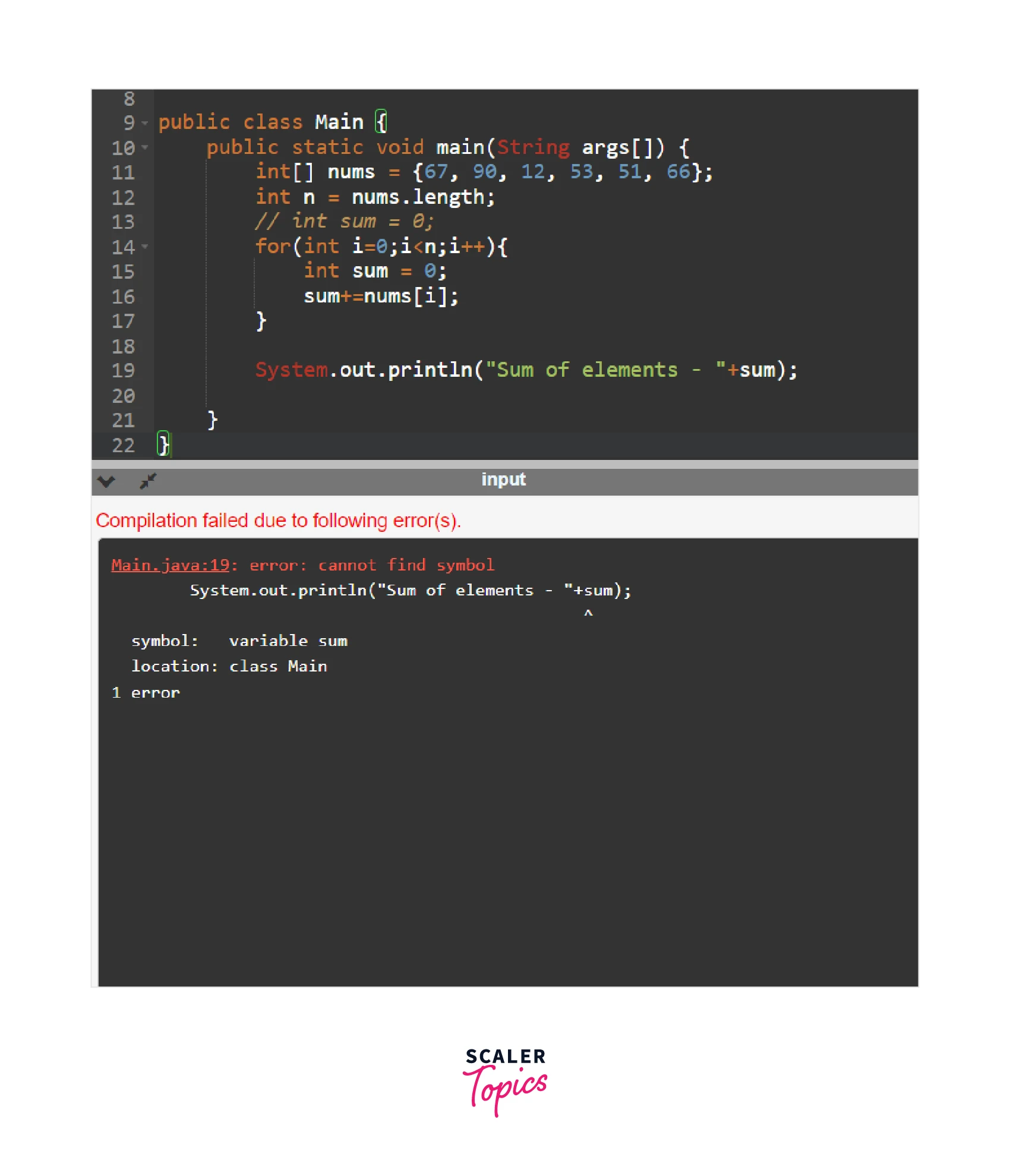
As we can see in the output, the compiler tells the line number of the error as well as points to the variable where the error occurred and the type of the error which is cannot find symbol in this case.
The compiler also produces the cannot find symbol including these two additional fields:
- The very first one is the symbol it is unable to find, i.e. the name and type of the referenced identifier.
- The other field is the location of the place where the symbol is used. The class and line number are returned where the identifier has been referenced.
Cannot Find Symbol vs Symbol Not Found vs Cannot Resolve Symbol
Different compilers may use slightly different terminologies. The ‘Cannot Find Symbol’, ‘Symbol Not Found’, and ‘Cannot Resolve Symbol’ are all same errors only. Besides the naming, these convey the same meaning to the user and the compiler.
Learn more about Java errors
Conclusion
- The ‘Cannot Find Symbol’ error in Java is a compilation error caused when the compiler cannot find a reference to an identifier.
- Silly mistakes like case sensitivity, use of underscore, use of undeclared variables, use of out-of-scope variables, etc. can cause this error.
- It is also identified by ‘Symbol Not Found’ and ‘Cannot Resolve Symbol’.
Whenever you need to use external classes/interfaces (either user defined or, built-in) in the current program you need to import those classes in your current program using the import keyword.
But, while importing any class −
-
If the path of the class/interface you are importing is not available to JVM.
-
If the absolute class name you have mentioned at the import statement is not accurate (including packages and class name).
-
If you have imported the class/interface used.
You will get an exception saying “Cannot find symbol ……”
Example
In the following example we are trying to read a string value representing the name of the user from key-board (System.in). For this we are using the scanner class of the Java.Util Package.
public class ReadingdData {
public static void main(String args[]) {
System.out.println("Enter your name: ");
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
String name = sc.next();
System.out.println("Hello "+name);
}
}
Compile time error
Since we are using a class named Scanner in our program and haven’t imported it in our program. On executing, this program generates the following compile time error −
ReadingdData.java:6: error: cannot find symbol
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
^
symbol: class Scanner
location: class ReadingdData
ReadingdData.java:6: error: cannot find symbol
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
^
symbol: class Scanner
location: class ReadingdData
2 errors
Solution
-
You need to set class path for the JAR file holding the required class interface.
-
Import the required class from the package using the import keyword. While importing you need to specify the absolute name (including the packages and sub packages) of the required class.
Example
Live Demo
import java.util.Scanner;
public class ReadingdData {
public static void main(String args[]) {
System.out.println("Enter your name: ");
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
String name = sc.next();
System.out.println("Hello "+name);
}
}
Output
Enter your name: krishna Hello krishna
import java.util.scanner;
import javax.swing.JOptionPane;
public class FirstHomeJavaApplet{
public static void main(String[] args){
int num1=2;
int num2=2;
int sum;
sum=num1+num2;
System.out.println("My first home practice of java applet");
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(null, num1 + "+" + num2 + " = " + sum, "Result of Addition",
JOptionPane.INFORMATION_MESSAGE);
}
}
This is my code but it is giving 1 error.I am using jdk 6 to run this applet.
The error is :cannot find symbol
symbol:class scanner
location:package java.util
import.java.util.scanner;
^
Thanks..
![]()
Thilo
254k99 gold badges501 silver badges648 bronze badges
asked Sep 26, 2010 at 6:33
Scanner should start with a capital S
answered Sep 26, 2010 at 6:35
0
By convention, Java classes start with capital letters. So it should be Scanner throughout. E.g.
import java.util.Scanner;
answered Sep 26, 2010 at 6:35
Matthew FlaschenMatthew Flaschen
274k50 gold badges513 silver badges537 bronze badges
0
See that your class name starts with a Capital letter java.util.Scanner; instead of java.util.scanner;
answered Sep 26, 2010 at 6:36
sushil bharwanisushil bharwani
29.3k30 gold badges92 silver badges128 bronze badges
0
Because the class name is Scanner not scanner.
answered Sep 26, 2010 at 6:36
ricsrics
5,4445 gold badges33 silver badges42 bronze badges
0
The class is called java.util.Scanner (with a capital S).
BalusC
1.1m370 gold badges3584 silver badges3535 bronze badges
answered Sep 26, 2010 at 6:36
![]()
ThiloThilo
254k99 gold badges501 silver badges648 bronze badges
0
Whenever you need to use external classes/interfaces (either user defined or, built-in) in the current program you need to import those classes in your current program using the import keyword.
But, while importing any class −
-
If the path of the class/interface you are importing is not available to JVM.
-
If the absolute class name you have mentioned at the import statement is not accurate (including packages and class name).
-
If you have imported the class/interface used.
You will get an exception saying “Cannot find symbol ……”
Example
In the following example we are trying to read a string value representing the name of the user from key-board (System.in). For this we are using the scanner class of the Java.Util Package.
public class ReadingdData {
public static void main(String args[]) {
System.out.println("Enter your name: ");
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
String name = sc.next();
System.out.println("Hello "+name);
}
}
Compile time error
Since we are using a class named Scanner in our program and haven’t imported it in our program. On executing, this program generates the following compile time error −
ReadingdData.java:6: error: cannot find symbol
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
^
symbol: class Scanner
location: class ReadingdData
ReadingdData.java:6: error: cannot find symbol
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
^
symbol: class Scanner
location: class ReadingdData
2 errors
Solution
-
You need to set class path for the JAR file holding the required class interface.
-
Import the required class from the package using the import keyword. While importing you need to specify the absolute name (including the packages and sub packages) of the required class.
Example
Live Demo
import java.util.Scanner;
public class ReadingdData {
public static void main(String args[]) {
System.out.println("Enter your name: ");
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
String name = sc.next();
System.out.println("Hello "+name);
}
}
Output
Enter your name: krishna Hello krishna
Возможно ошибка
com/javarush/task/task03/task0318/Solution.java:12: error: cannot find symbol
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
^
symbol: class Scanner
location: class com.javarush.task.task03.task0318.Solution
com/javarush/task/task03/task0318/Solution.java:12: error: cannot find symbol
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
^
symbol: class Scanner
location: class com.javarush.task.task03.task0318.Solution
Вот ошибка которую выдаёт компилятор.Подскажите какой import нужно добавить что бы компилятор мог закомпилировать или может у меня тут ошибка буду рад если исправите меня
package com.javarush.task.task03.task0318;
/*
План по захвату мира
*/
import java.io.*;
public class Solution {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
String name = scanner.nextLine();
int age = scanner.nextInt();
System.out.println(name + «захватим мир через » + age+ » лет. Му-ха-ха!»);
}
}
Этот веб-сайт использует данные cookie, чтобы настроить персонально под вас работу сервиса. Используя веб-сайт, вы даете согласие на применение данных cookie. Больше подробностей — в нашем Пользовательском соглашении.
Symbols and Symbol Table
Before diving into the details of the “cannot find a symbol” error, here is a brief introduction to symbols and symbol tables in Java. A symbol refers to an identifier in the compilation process in Java. All the identifiers used in the source code are collected into a symbol table in the lexical analysis stage. The symbol table is a very significant data structure created and maintained by the compilers to store all the identifiers and their information.
This information is entered into the symbol tables during lexical and syntax analysis which is then used in multiple phases of compilation.
From classes, variables, interfaces to methods, all of them require an identifier for declaration. During the code generation process, when these identifiers are encountered in the source code, the compiler checks for them in the symbol tables and the stored information is then used to verify the declarations, the scope of a variable, and verifying that the expression is semantically correct or not.
The compilation process usually does not go as smooth as you would think. Errors are inevitable in any development stage and one of the very commonly occurring errors during the compilation process is Java “cannot Find Symbol” Error. In this article, we will be discussing the reasons behind the occurrence of Java cannot find symbol errors and how you can resolve them.
As the name suggests, the Java cannot find symbol error occurs when a required symbol cannot be found in the symbol table. Although there can be various reasons behind this, it points to one fact the Java compiler was unable to find the symbol and its details associated with a given identifier.
As there are a variety of Java compilers available, many of them use slightly different terminologies, because of that, you can also find the “cannot find symbol” error termed as the “symbol not found” or “cannot resolve symbol” error. Besides the name, there is simply no difference between these errors.
Structure of Java Cannot Find Symbol Error
The compiler output a specific error message with the cannot find symbol error.
It contains the following two fields that indicate the missing symbol and its location:
- Symbol: The name and type of the identifier you are looking for.
- Location: The particular class in which that identifier has been referenced.
Causes of Java Cannot Find Symbol Error
We will be discussing the following most common causes of the cannot find symbol error during compilation,
- misspelt identifiers
- Undeclared variables
- Out of scope references to variables and methods
- The unintentional omission of import statements
Misspelt identifier names
This is the most common and most occurring reason behind the Java cannot find symbol error. Misspelling an existing variable, class, interface, package name or a method causes the “cannot find symbol error” as the compiler cannot recognize the symbol and identifies it as an undeclared variable. Java identifiers are also case-sensitive, so even a slight variation of an existing variable will result in this error.
See code example below:
1. public class MisspelledMethodNameExample {
2. static int findLarger(int n1, int n2) {
3. if (n1 > n2) return n1;
4. if (n2 > n11) return n2;
5. if (n2 == n11) return -1;
6. }
7.
8. public static void main(String... args) {
9. int value = findlarger(20, 4); // findlarger ≠ findLarger
10. System.out.println(value);
11. }
12. }
MisspelledMethodNameExample.java:9: error: cannot find symbol int value = Fibonacci(20); ^ symbol: method findLarger(int, int) location: class MisspelledMethodNameExample
It can be easily resolved by correcting the spelling of the function in line 9.
Undeclared variables
When the Java compiler come across an identifier used in the code but it cannot be found in the symbol table, the “cannot find symbol” error is shown. The only reason behind the absence of a variable from the symbol table is that it is not declared in the code. Some new programming languages do not require explicit declaration of variables but it is mandatory in Java to always declare a variable before it is used or referenced in the source code.
The code snippet below demonstrates an undeclared variable in the code. In this case, the identifier sum on line 7, causes the Java “cannot find symbol error”.
See code example below:
1. public class UndeclaredVariableExample
2. {
3. public static void main(String... args) {
4. int num1 = 5;
5. int num2 = 10;
6. int num3 = 43;
7. sum = (num1 + num2 + num3) // sum is not declared
8. System.out.println(sum);
9. }
10. }
UndeclaredVariableExample.java:7: error: cannot find symbol sum = (num1 + num2 + num3); ^ symbol: variable sum location: class UndeclaredVariableExample UndeclaredVariableExample.java:8: error: cannot find symbol System.out.println(sum); ^ symbol: variable sum location: class UndeclaredVariableExample 2 errors
Declaring this variable by specifying the appropriate data type can easily resolve the error.
See this corrected code below,
1. public class UndeclaredVariableExample
2. {
3. public static void main(String args) {
4. int num1 = 5;
5. int num2 = 10;
6. int num3 = 43;
7.
8. int sum = (num1 + num2 + num3);
9. System.out.println(sum);
10. }
11. }
Out of scope variable
When a Java code attempts to access a variable declared out of scope such as in a non-inherited scope the compiler will result in issuing the “cannot find symbol” error. This commonly happens when you attempt to access a variable declared inside a method or a loop, from outside of the method.
See this code example below where the “cannot find symbol” error has occurred when the counter variable which is declared inside a for loop is attempted to be accessed from out of the loop.
See code below:
1. public class OutOfScopeExample
2. {
3. public static void main(String args) {
4.
5. for (int counter = 0; counter < 100; counter++)
6. { … }
7.
8. System.out.println(“Even numbers from 0 to 100”)
9. if (counter mod 2 == 0)
10. {
11. System.out.println(counter);
12. }
13. }
14. }
OutOfScopeVariableExample.java:9: error: cannot find symbol if (counter mod 2 == 0) ^ symbol: variable counter location: class OutOfScopeVariableExample OutOfScopeVariableExample.java:12: error: cannot find symbol System.out.println(counter); ^ symbol: variable counter location: class OutOfScopeVariableExample 2 errors
I can be easily resolved by just moving the if block inside the for loop (local scope).
See this code example,
1. public class OutOfScopeExample
2. {
3. public static void main(String... args) {
4.
5. for (int counter = 0; counter < 100; counter++)
6. {
7. System.out.println(“Even numbers from 0 to 100”)
8. if (counter mod 2 == 0)
9. {
10. System.out.println(counter);
11. }
12. }
13. }
14. }
Missing import statement
Java allows you to use built-in classes or any imported libraries in your code to save your time by reusing the code but it requires importing them properly using the import statements at the start. Missing the import statement in your code will result in the cannot find symbol error.
java.util.Math class is utilized in the code given below but it is not declared with the “import” keyword, resulting in the “cannot find symbol error”.
See code below:
1. public class MissingImportExample {
2.
3. public static void main(String args)
4. {
5. double sqrt19 = Math.sqrt(19);
6. System.out.println("sqrt19 = " + sqrt19);
7. }
8. }
MissingImportExample.java:6: error: cannot find symbol double sqrt19 = Math.sqrt(19); ^ symbol: class Math location: class MissingImportExample
Adding the missing import statement can easily solve the issue, see code below:
1. import java.util.Math;
2.
3. public class MissingImporExample {
4.
5. public static void main(String args)
6. {
7. double sqrt19 = Math.sqrt(19);
8. System.out.println("sqrt19 = " + sqrt19);
9. }
10. }
Miscellaneous reasons
We have covered some of the main causes of the “cannot find symbol” Java error but occasionally it can also result due to some unexpected reasons. One such case is when attempting to create an object without the new keyword or an accidental semicolon at the wrong place that would terminate the statement at an unexpected point.
Also Read: Functional Interfaces In Java
Some other causes for the cannot find symbol error may include when you forget to recompile the code or you end up using the dependencies with an incompatible version of Java. Building a project with a very old JDK version can also be a reason as well as mistakenly redefining platform or library classes with the same identifier.
Conclusion
We have discussed that the “cannot find symbol Java” error is a Java compile-time error which is encountered whenever an identifier in the source code is not identified by the compiler. Similar to any other compilation error, it is very significant to understand the causes of this error, so that you can easily pinpoint the issue and address it properly.
Once you can discover the reason behind the error, it can be easily resolved as demonstrated by various examples in this article.
I’ve posted about this code earlier today but for a different reason. I honestly have zero clue what to do. I feel like i’ve tried everything. Pls help.
Here is my code:
// Imports
import static java.lang.System.*;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class TheKingsGuard{
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner sc = new Scanner([System.in](https://System.in));
// Variable Defines
String Knight = «Knight»;
String Archer = «Archer»;
String Mage = «Mage»;
String Sword = «Sword»;
String Axe = «Axe»;
String Mace = «Mace»;
String Bow = «Bow»;
String Crossbow = «Crossbow»;
String Staff = «Staff»;
String Wand = «Wand»;
// Program Header
System.out.println(«Hello and welcome to The King’s Guard!»);
System.out.println(«To start, please enter your characters details bellow:»);
System.out.println(«»);
// Character Sheet
// Character Name
System.out.println(«Character Name:»);
String Name = sc.nextLine () ;
// Class Choose
System.out.println(«Choose a class (Knight, Archer or Mage):»);
String Class = sc.nextLine () ;
while (!Class.equals("Knight") && !Class.equals("Archer") && !Class.equals("Mage")) {
System.out.println("That is not a valid class.");
}
// Choose Weapon
if (Class.equals («Knight»)){
System.out.println(«Choose a weapon (Sword, Axe or Mace):»);
String Weapon = sc.nextLine () ;
}
if (!Weapon.equals(«Sword») && !Weapon.equals(«Axe») && !Weapon.equals(«Mace»)) {
System.out.println(«That is not a valid weapon.»); }
do {System.out.println("Choose a weapon again (Sword, Axe or Mace):");
String Weapon = sc.nextLine () ;}
while (!Weapon.equals("Sword") && !Weapon.equals("Axe") && !Weapon.equals("Mace")) ;
if (Class.equals («Archer»)) {
System.out.println(«Choose a weapon (Bow or Crossbow):»);
String Weapon = sc.nextLine () ;
}
if (!Weapon.equals(«Bow») && !Weapon.equals(«Crossbow»)) {
System.out.println(«That is not a valid weapon.»);
}
do {System.out.println(«Choose a weapon again (Bow or Crossbow):»);
String Weapon = sc.nextLine () ;}
while (!Weapon.equals(«Bow») && !Weapon.equals(«Crossbow»)) ;
if (Class.equals ("Mage")) {
System.out.println("Choose a weapon (Staff or Wand):");
String Weapon = sc.nextLine () ;
}
if (!Weapon.equals("Staff") && !Weapon.equals("Wand")) {
System.out.println("That is not a valid weapon.");
}
do {System.out.println(«Choose a weapon again (Wand or Staff):»);
String Weapon = sc.nextLine () ;}
while (!Weapon.equals("Wand") && !Weapon.equals("Staff")) ;
// Verb Define
}
}
Here is the error report:
TheKingsGuard.java:47: error: cannot find symbol
string Weapon = sc.nextLine () ;
^
symbol: class string
location: class TheKingsGuard
TheKingsGuard.java:49: error: cannot find symbol
if (!Weapon.equals(«Sword») && !Weapon.equals(«Axe») && !Weapon.equals(«Mace»)) {
^
symbol: variable Weapon
location: class TheKingsGuard
TheKingsGuard.java:49: error: cannot find symbol
if (!Weapon.equals(«Sword») && !Weapon.equals(«Axe») && !Weapon.equals(«Mace»)) {
^
symbol: variable Weapon
location: class TheKingsGuard
TheKingsGuard.java:49: error: cannot find symbol
if (!Weapon.equals(«Sword») && !Weapon.equals(«Axe») && !Weapon.equals(«Mace»)) {
^
symbol: variable Weapon
location: class TheKingsGuard
TheKingsGuard.java:55: error: cannot find symbol
while (!Weapon.equals(«Sword») && !Weapon.equals(«Axe») && !Weapon.equals(«Mace»)) ;
^
symbol: variable Weapon
location: class TheKingsGuard
TheKingsGuard.java:55: error: cannot find symbol
while (!Weapon.equals(«Sword») && !Weapon.equals(«Axe») && !Weapon.equals(«Mace»)) ;
^
symbol: variable Weapon
location: class TheKingsGuard
TheKingsGuard.java:55: error: cannot find symbol
while (!Weapon.equals(«Sword») && !Weapon.equals(«Axe») && !Weapon.equals(«Mace»)) ;
^
symbol: variable Weapon
location: class TheKingsGuard
TheKingsGuard.java:63: error: cannot find symbol
if (!Weapon.equals(«Bow») && !Weapon.equals(«Crossbow»)) {
^
symbol: variable Weapon
location: class TheKingsGuard
TheKingsGuard.java:63: error: cannot find symbol
if (!Weapon.equals(«Bow») && !Weapon.equals(«Crossbow»)) {
^
symbol: variable Weapon
location: class TheKingsGuard
TheKingsGuard.java:69: error: cannot find symbol
while (!Weapon.equals(«Bow») && !Weapon.equals(«Crossbow»)) ;
^
symbol: variable Weapon
location: class TheKingsGuard
TheKingsGuard.java:69: error: cannot find symbol
while (!Weapon.equals(«Bow») && !Weapon.equals(«Crossbow»)) ;
^
symbol: variable Weapon
location: class TheKingsGuard
TheKingsGuard.java:76: error: cannot find symbol
if (!Weapon.equals(«Staff») && !Weapon.equals(«Wand»)) {
^
symbol: variable Weapon
location: class TheKingsGuard
TheKingsGuard.java:76: error: cannot find symbol
if (!Weapon.equals(«Staff») && !Weapon.equals(«Wand»)) {
^
symbol: variable Weapon
location: class TheKingsGuard
TheKingsGuard.java:82: error: cannot find symbol
while (!Weapon.equals(«Wand») && !Weapon.equals(«Staff»)) ;
^
symbol: variable Weapon
location: class TheKingsGuard
TheKingsGuard.java:82: error: cannot find symbol
while (!Weapon.equals(«Wand») && !Weapon.equals(«Staff»)) ;
^
symbol: variable Weapon
location: class TheKingsGuard
15 errors
