Коллеги добрый день.
На одном из серверов появляется данное сообщение:
Аудит отказа
Учетной записи не удалось выполнить вход в систему.
Субъект:
ИД безопасности: NULL SID
Имя учетной записи: —
Домен учетной записи: —
Код входа: 0x0
Тип входа: 3
Учетная запись, которой не удалось выполнить вход:
ИД безопасности: NULL SID
Имя учетной записи: fortest
Домен учетной записи: RUSSLAVBANK
Сведения об ошибке:
Причина ошибки: Ошибка при входе.
Состояние: 0xc00002ee
Подсостояние: 0x0
Сведения о процессе:
Идентификатор процесса вызывающей стороны: 0x0
Имя процесса вызывающей стороны: —
Сведения о сети:
Имя рабочей станции: —
Сетевой адрес источника: —
Порт источника: —
Сведения о проверке подлинности:
Процесс входа: Kerberos
Пакет проверки подлинности: Kerberos
Промежуточные службы: —
Имя пакета (только NTLM): —
Длина ключа: 0
Данное событие возникает при неудачной попытке входа. Оно регистрируется на компьютере, попытка доступа к которому была выполнена.
Поля «Субъект» указывают на учетную запись локальной системы, запросившую вход. Обычно это служба, например, служба «Сервер», или локальный процесс, такой как Winlogon.exe или Services.exe.
В поле «Тип входа» указан тип выполненного входа. Наиболее распространенными являются типы 2 (интерактивный) и 3 (сетевой).
В полях «Сведения о процессе» указано, какая учетная запись и процесс в системе выполнили запрос на вход.
Поля «Сведения о сети» указывают на источник запроса на удаленный вход. Имя рабочей станции доступно не всегда, и в некоторых случаях это поле может оставаться незаполненным.
Поля сведений о проверке подлинности содержат подробные данные о конкретном запросе на вход.
— В поле «Промежуточные службы» указано, какие промежуточные службы участвовали в данном запросе на вход.
— Поле «Имя пакета» указывает на подпротокол, использованный с протоколами NTLM.
— Поле «Длина ключа» содержит длину созданного ключа сеанса. Это поле может иметь значение «0», если ключ сеанса не запрашивался.
Что мы сделали:
Подняли уровень домена и леса до Windows Server 2008 R2
Мы точно не знаем, связано это с этим или нет. Но после данной операции клиенты на которых установлена Windows XP SP3 (SP2) не могут подключиться к серверу (Windows Server 2008 R2)
Пользователи Windows 7 (Windows Server 2008 2008 R2) могут подключиться.
На сервере нечего не делали, никаких Firewall между клиентом и сервером нет.
Наверное что-то с политикой. Типо подписывания SMB или что-то ещё.
С клиентов Windows XP можем подключиться к этому серверу по RDP и по SMB (видим шары)
Сломали голову и не знаем что делать.
Прошу помощи господа. Спасибо за ранее.
Delete saved passwords from old cache to login again
by Claire Moraa
Claire likes to think she’s got a knack for solving problems and improving the quality of life for those around her. Driven by the forces of rationality, curiosity,… read more
Updated on February 13, 2023
Reviewed by
Alex Serban

After moving away from the corporate work-style, Alex has found rewards in a lifestyle of constant analysis, team coordination and pestering his colleagues. Holding an MCSA Windows Server… read more
- Event ID 4625 is a security event that indicates that the user account failed to log on.
- The most common cause is that your account’s password has expired, and you have not changed it yet.
- To avoid such errors, ensure your password is up-to-date and your user account has the administrative privileges to logon.
XINSTALL BY CLICKING THE DOWNLOAD FILE
Fortect is a tool that does not simply cleans up your PC, but has a repository with several millions of Windows System files stored in their initial version. When your PC encounters a problem, Fortect will fix it for you, by replacing bad files with fresh versions. To fix your current PC issue, here are the steps you need to take:
- Download Fortect and install it on your PC.
- Start the tool’s scanning process to look for corrupt files that are the source of your problem
- Right-click on Start Repair so the tool could start the fixing algorythm
- Fortect has been downloaded by 0 readers this month.
Accessing the Windows Server can sometimes be a hassle, even for verified users. Sometimes, it’s the Windows Server Manager that’s not opening, while other times, you get a logon error dubbed Event ID 4625.
In such cases, it’s usually your password that is probably expired, so an update should do the trick. However, if that does not work, read on to find out how to bypass this logon failure.
What is Event ID 4625 failure reason?
The Event ID 4625 is a logon error that occurs when you try to access the Windows server. If accompanied by Event ID 4625 status 0xc00006d, you’ll know it’s a bad password.
Typically, this occurs because the system uses a cached password rather than an updated one you entered. This is because of how Windows stores password in a database.
When you log into a domain, it looks at this database to determine what your account’s password is. If it finds a match, then it just uses the stored version instead of prompting you for one.
Other reasons for this error include:
- Insufficient permissions – The user may not have sufficient permissions to perform the action, or the Active Directory has been corrupted. Always check for Event ID 4625 null SID, as it will let you know whether it was a valid account.
- Workstation restriction – A workstation restriction is an action that restricts the ability of a user to log on locally.
- Change of accounts – This can happen if you use a domain account to log on to a computer and then log in with a local account. It can also occur if you change from a local account to a domain account or vice versa.
- Logon Process from an untrusted logon processes list – User accounts are usually added to the Trusted Logons Group. If you get a logon error, the logon process has not been validated by the security system.
- Account expiry – If the user account hasn’t been used for a long time, you may get the username does not exist error. It’s possible that the account has been marked as inactive by AD and needs reactivation.
How can I fix Event ID 4625 logon error?
Before you attempt any of the recommended solutions below, ensure you check the following:
- Check that you have not misspelled your password.
- Clear any cache that may contain any expired saved passwords.
- Verify that the account you’re using to log on has enough privileges.
- Check whether there’s a mismatch between the logon type and the account you’re using to logon.
- Ensure you’re not using an account restricted to an internal IP address.
- Confirm from your Administrator that your account is still active.
1. Rejoin the domain
- Hit the Windows + R keys to open the Run command.
- Type regedit in the dialog box and hit Enter.
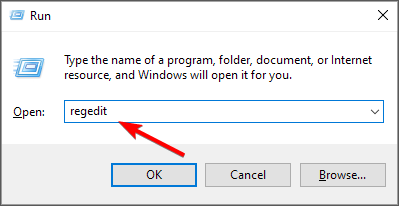
- Navigate to the following location:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESYSTEMCurrentControlSetControlLsa - Right-click on an empty space on the right and rename it as a NEW DWORD (32-bit) as LmCompatibilityLevel.
- Double-click on it and set the Value data as 1.
- Restart your PC and try logging in again.
2. Remove hidden credentials
- Hit the Windows key, type cmd in the search bar, and click Open.
- Type the following commands and hit Enter after each one:
psexec -i -s -d cmd.exerundll32 keyngr.dll KRShowKeyMgr - A list of stored usernames and passwords will appear. Delete them from your server and restart your PC.
Some PC issues are hard to tackle, especially when it comes to missing or corrupted system files and repositories of your Windows.
Be sure to use a dedicated tool, such as Fortect, which will scan and replace your broken files with their fresh versions from its repository.
The logon types should provide more detail to help you narrow the type of failure. If you get the Event ID 4625 logon type 3, Event ID 4625 logon type 4, or Event ID 4625 logon type 8, you should be able to get more information on where the user tried to log in from.
- Fix: Remote Desktop Services is Currently Busy Error
- What is Event ID 800 & How to Quickly Fix It
- Event ID 5137: A Directory Service Object Was Created [Fix]
- Event ID: 10036 Distributed COM [Fix]
3. Disable NTLM logins
- Hit the Windows + R keys to open the Run command.
- Type secpol.msc in the dialog box and hit Enter.
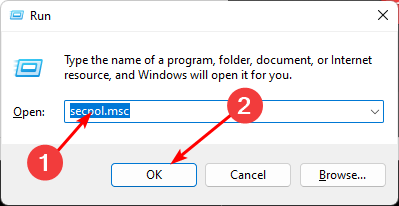
- Navigate to the following location:
Local policies/Security options/Network security: Restrict NTLM: Incoming NTLM traffic - Double-click on Network security: Restrict NTLM: Incoming NTLM traffic, and in the drop-down menu, select deny all accounts, then press Apply, then OK to save changes.
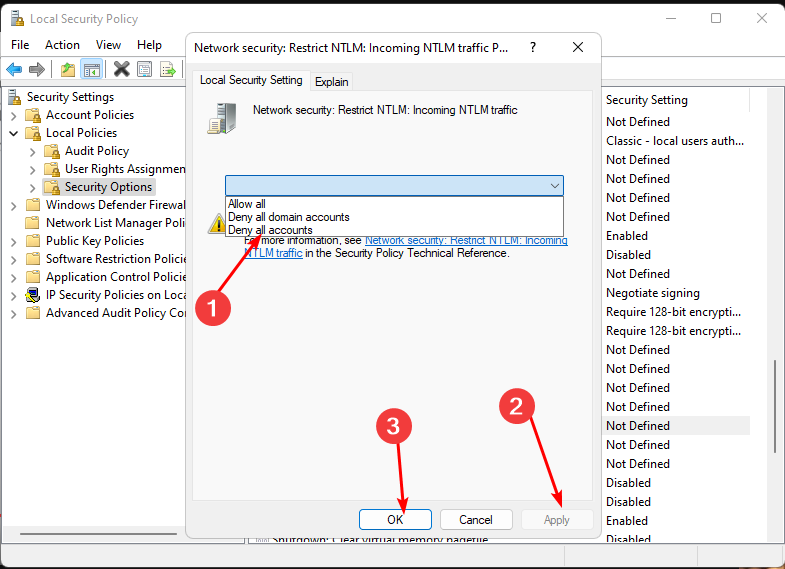
NTLM is an authentication protocol used by Windows systems to provide additional security when users access resources on a network. It can authenticate users against an Active Directory domain controller without supplying a password.
However, it’s also the most easily attacked authentication protocol and can be disabled for improved security.
The most common reason administrators disable NTLM authentication on their servers is that users have trouble logging into their systems when they are away from their offices or behind a proxy server.
For maximum security on your Windows Server, we recommend that you enable the TLS protocol and avoid outdated versions with known vulnerabilities.
Elsewhere, you may also encounter the Event ID 4768 error, so be sure to check out our detailed guide for various fixes.
Please let us know if you have any additional solutions in the comment section below.
Still experiencing issues?
SPONSORED
If the above suggestions have not solved your problem, your computer may experience more severe Windows troubles. We suggest choosing an all-in-one solution like Fortect to fix problems efficiently. After installation, just click the View&Fix button and then press Start Repair.
![]()
Время на прочтение
4 мин
Количество просмотров 256K

Рэнди Франклин Смит (CISA, SSCP, Security MVP) имеет в своем арсенале очень полезный документ, рассказывающий о том, какие события (event IDs) обязательно должны отслеживаться в рамках обеспечения информационной безопасности Windows. В этом документе изложена крайне полезная информация, которая позволит Вам “выжать” максимум из штатной системы аудита. Мы подготовили перевод этого материала. Заинтересованных приглашаем под кат.
О том, как настроить аудит, мы уже обстоятельно писали в одном из наших постов. Но из всех event id, которые встречаются в журналах событий, необходимо остановить свое внимание на нескольких критических важных. На каких именно – решать каждому. Однако Рэнди Франклин Смит предлагает сосредоточить внимание на 10 важных событиях безопасности в Windows.
Контроллеры доменов
Event ID — (Категория) — Описание
1) 675 или 4771
(Аудит событий входа в систему)
Событие 675/4771 на контроллере домена указывает на неудачную попытку войти через Kerberos на рабочей станции с доменной учетной записью. Обычно причиной этого является несоответствующий пароль, но код ошибки указывает, почему именно аутентификация была неудачной. Таблица кодов ошибок Kerberos приведена ниже.
2) 676, или Failed 672 или 4768
(Аудит событий входа в систему)
Событие 676/4768 логгируется для других типов неудачной аутентификации. Таблица кодов Kerberos приведена ниже.
ВНИМАНИЕ: В Windows 2003 Server событие отказа записывается как 672 вместо 676.
3) 681 или Failed 680 или 4776
(Аудит событий входа в систему)
Событие 681/4776 на контроллере домена указывает на неудачную попытку входа в систему через
NTLM с доменной учетной записью. Код ошибки указывает, почему именно аутентификация была неудачной.
Коды ошибок NTLM приведены ниже.
ВНИМАНИЕ: В Windows 2003 Server событие отказа записывается как 680 вместо 681.
4) 642 или 4738
(Аудит управления учетными записями)
Событие 642/4738 указывает на изменения в указанной учетной записи, такие как сброс пароля или активация деактивированной до этого учетной записи. Описание события уточняется в соответствие с типом изменения.
5) 632 или 4728; 636 или 4732; 660 или 4756
(Аудит управления учетными записями)
Все три события указывают на то, что указанный пользователь был добавлен в определенную группу. Обозначены Глобальная (Global), Локальная (Local) и Общая (Universal) соответственно для каждого ID.
6) 624 или 4720
(Аудит управления учетными записями)
Была создана новая учетная запись пользователя
7) 644 или 4740
(Аудит управления учетными записями)
Учетная запись указанного пользователя была заблокирована после нескольких попыток входа
 517 или 1102
517 или 1102
(Аудит системных событий)
Указанный пользователь очистил журнал безопасности
Вход и выход из системы (Logon/Logoff)
Event Id — Описание
528 или 4624 — Успешный вход в систему
529 или 4625 — Отказ входа в систему – Неизвестное имя пользователя или неверный пароль
530 или 4625 Отказ входа в систему – Вход в систему не был осуществлен в течение обозначенного периода времени
531 или 4625 — Отказ входа в систему – Учетная запись временно деактивирована
532 или 4625 — Отказ входа в систему – Срок использования указанной учетной записи истек
533 или 4625 — Отказ входа в систему – Пользователю не разрешается осуществлять вход в систему на данном компьютере
534 или 4625 или 5461 — Отказ входа в систему – Пользователь не был разрешен запрашиваемый тип входа на данном компьютере
535 или 4625 — Отказ входа в систему – Срок действия пароля указанной учетной записи истек
539 или 4625 — Отказ входа в систему – Учетная запись заблокирована
540 или 4624 — Успешный сетевой вход в систему (Только Windows 2000, XP, 2003)
Типы входов в систему (Logon Types)
Тип входа в систему — Описание
2 — Интерактивный (вход с клавиатуры или экрана системы)
3 — Сетевой (например, подключение к общей папке на этом компьютере из любого места в сети или IIS вход — Никогда не заходил 528 на Windows Server 2000 и выше. См. событие 540)
4 — Пакет (batch) (например, запланированная задача)
5 — Служба (Запуск службы)
7 — Разблокировка (например, необслуживаемая рабочая станция с защищенным паролем скринсейвером)
8 — NetworkCleartext (Вход с полномочиями (credentials), отправленными в виде простого текст. Часто обозначает вход в IIS с “базовой аутентификацией”)
9 — NewCredentials
10 — RemoteInteractive (Терминальные службы, Удаленный рабочий стол или удаленный помощник)
11 — CachedInteractive (вход с кешированными доменными полномочиями, например, вход на рабочую станцию, которая находится не в сети)
Коды отказов Kerberos
Код ошибки — Причина
6 — Имя пользователя не существует
12 — Ограничение рабочей машины; ограничение времени входа в систему
18 — Учетная запись деактивирована, заблокирована или истек срок ее действия
23 — Истек срок действия пароля пользователя
24 — Предварительная аутентификация не удалась; обычно причиной является неверный пароль
32 — Истек срок действия заявки. Это нормальное событие, которое логгируется учетными записями компьютеров
37 — Время на рабочей машины давно не синхронизировалось со временем на контроллере домена
Коды ошибок NTLM
Код ошибки (десятичная система) — Код ошибки (16-ричная система) — Описание
3221225572 — C0000064 — Такого имени пользователя не существует
3221225578 — C000006A — Верное имя пользователя, но неверный пароль
3221226036 — C0000234 — Учетная запись пользователя заблокирована
3221225586 — C0000072 — Учетная запись деактивирована
3221225583 — C000006F — Пользователь пытается войти в систему вне обозначенного периода времени (рабочего времени)
3221225584 — C0000070 — Ограничение рабочей станции
3221225875 — C0000193 — Истек срок действия учетной записи
3221225585 — C0000071 — Истек срок действия пароля
3221226020 — C0000224 — Пользователь должен поменять пароль при следующем входе в систему
Еще раз продублируем ссылку на скачивание документа на сайте Рэнди Франклина Смита www.ultimatewindowssecurity.com/securitylog/quickref/Default.aspx. Нужно будет заполнить небольшую форму, чтобы получить к нему доступ.
P.S. Хотите полностью автоматизировать работу с журналами событий? Попробуйте новую версию NetWrix Event Log Manager 4.0, которая осуществляет сбор и архивирование журналов событий, строит отчеты и генерирует оповещения в режиме реального времени. Программа собирает данные с многочисленных компьютеров сети, предупреждает Вас о критических событиях и централизованно хранит данные обо всех событиях в сжатом формате для удобства анализа архивных данных журналов. Доступна бесплатная версия программы для 10 контроллеров доменов и 100 компьютеров.
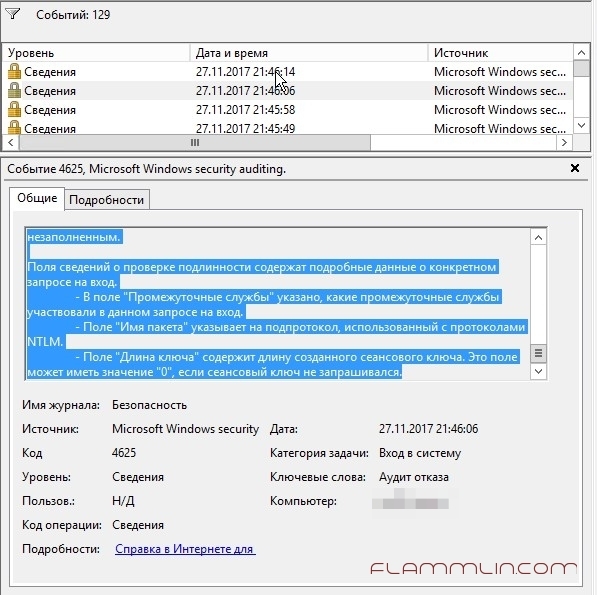
Уже с год наблюдаю ошибку в логах 4625, ошибка связанная с попыткой входа по RDP. Но к сожалению в логах увидеть кто и откуда не представляется возможным.
В логах постоянно вот такая штука появлялась:
Событие 4625 (Event ID 4625 no ip)
Учетной записи не удалось выполнить вход в систему. Субъект: ИД безопасности: NULL SID Имя учетной записи: – Домен учетной записи: – Код входа: 0x0 Тип входа: 3 Учетная запись, которой не удалось выполнить вход: ИД безопасности: NULL SID Имя учетной записи: АДМИНИСТРАТОР Домен учетной записи: Сведения об ошибке: Причина ошибки: Неизвестное имя пользователя или неверный пароль. Состояние: 0xC000006D Подсостояние: 0xC000006A Сведения о процессе: Идентификатор процесса вызывающей стороны: 0x0 Имя процесса вызывающей стороны: – Сведения о сети: Имя рабочей станции: – Сетевой адрес источника: – Порт источника: – Сведения о проверке подлинности: Процесс входа: NtLmSsp Пакет проверки подлинности: NTLM Промежуточные службы: – Имя пакета (только NTLM): – Длина ключа: 0 Данное событие возникает при неудачной попытке входа. Оно регистрируется на компьютере, попытка доступа к которому была выполнена. Поля “Субъект” указывают на учетную запись локальной системы, запросившую вход. Обычно это служба, например, служба “Сервер”, или локальный процесс, такой как Winlogon.exe или Services.exe. В поле “Тип входа” указан тип выполненного входа. Наиболее распространенными являются типы 2 (интерактивный) и 3 (сетевой). В полях “Сведения о процессе” указано, какая учетная запись и процесс в системе выполнили запрос на вход. Поля “Сведения о сети” указывают на источник запроса на удаленный вход. Имя рабочей станции доступно не всегда, и в некоторых случаях это поле может оставаться незаполненным. Поля сведений о проверке подлинности содержат подробные данные о конкретном запросе на вход. – В поле “Промежуточные службы” указано, какие промежуточные службы участвовали в данном запросе на вход. – Поле “Имя пакета” указывает на подпротокол, использованный с протоколами NTLM. – Поле “Длина ключа” содержит длину созданного сеансового ключа. Это поле может иметь значение “0”, если сеансовый ключ не запрашивался.
[свернуть]
Периодичность таких ошибок ничем не связана. Может за раз появиться только один раз, может наоборот под 200 штук набежать. По началу думал, что проблема в сети, мол клиент какой то лезет, но проверив методом исключений, я понял. Клиент был и был он снаружи, а это значит что мы имеем самый настоящий bruteforce.
Помогла утилита Cyberarms IDDS, которая прекрасно смогла отобразить ip адрес недоброжелателя и окончательно понять, что он снаружи ломится на сервак.
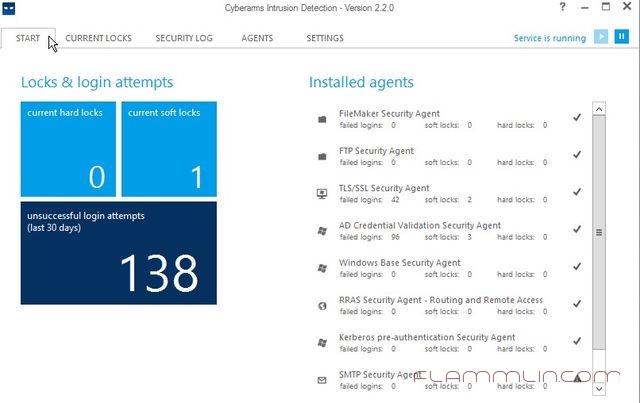
Программа достаточна проста в настройке и дополнительных знаний не требует. Необходимо сразу произвести настройку мониторинга присутствующих агентов и просто закрыть, так как программа работает как служба.
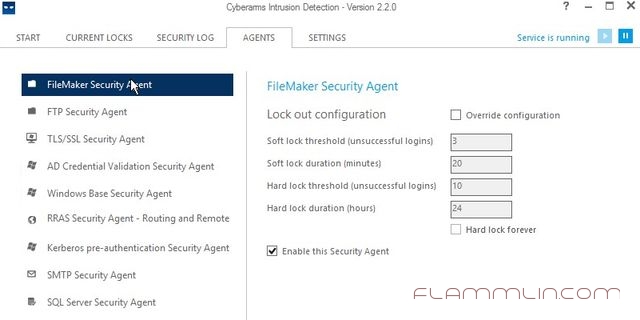
Не забываем проставлять напротив интересующих нас “служб” галочку Enable и жать кнопку Save.
В итоге работы получил вот такой отчет:
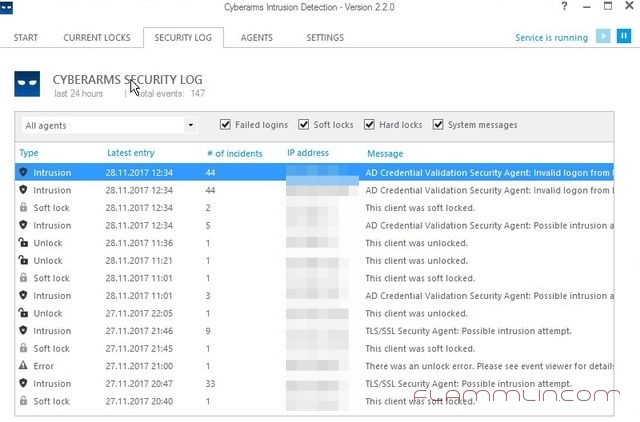
Cyberarms IDDS работает с правилами Windows FireWall и нежелательные лица добавляет туда.
| title | description | ms.pagetype | ms.prod | ms.mktglfcycl | ms.sitesec | ms.localizationpriority | author | ms.date | ms.reviewer | manager | ms.author | ms.technology | ms.collection | ms.topic | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
4625(F) An account failed to log on. |
Describes security event 4625(F) An account failed to log on. This event is generated if an account logon attempt failed for a locked out account. |
security |
windows-client |
deploy |
library |
none |
vinaypamnani-msft |
01/03/2022 |
aaroncz |
vinpa |
itpro-security |
|
reference |
4625(F): An account failed to log on.

Subcategories: Audit Account Lockout and Audit Logon
Event Description:
This event is logged for any logon failure.
It generates on the computer where logon attempt was made, for example, if logon attempt was made on user’s workstation, then event will be logged on this workstation.
This event generates on domain controllers, member servers, and workstations.
[!NOTE]
For recommendations, see Security Monitoring Recommendations for this event.
Event XML:
- <Event xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/win/2004/08/events/event"> - <System> <Provider Name="Microsoft-Windows-Security-Auditing" Guid="{54849625-5478-4994-A5BA-3E3B0328C30D}" /> <EventID>4625</EventID> <Version>0</Version> <Level>0</Level> <Task>12546</Task> <Opcode>0</Opcode> <Keywords>0x8010000000000000</Keywords> <TimeCreated SystemTime="2015-09-08T22:54:54.962511700Z" /> <EventRecordID>229977</EventRecordID> <Correlation /> <Execution ProcessID="516" ThreadID="3240" /> <Channel>Security</Channel> <Computer>DC01.contoso.local</Computer> <Security /> </System> - <EventData> <Data Name="SubjectUserSid">S-1-5-18</Data> <Data Name="SubjectUserName">DC01$</Data> <Data Name="SubjectDomainName">CONTOSO</Data> <Data Name="SubjectLogonId">0x3e7</Data> <Data Name="TargetUserSid">S-1-0-0</Data> <Data Name="TargetUserName">Auditor</Data> <Data Name="TargetDomainName">CONTOSO</Data> <Data Name="Status">0xc0000234</Data> <Data Name="FailureReason">%%2307</Data> <Data Name="SubStatus">0x0</Data> <Data Name="LogonType">2</Data> <Data Name="LogonProcessName">User32</Data> <Data Name="AuthenticationPackageName">Negotiate</Data> <Data Name="WorkstationName">DC01</Data> <Data Name="TransmittedServices">-</Data> <Data Name="LmPackageName">-</Data> <Data Name="KeyLength">0</Data> <Data Name="ProcessId">0x1bc</Data> <Data Name="ProcessName">C:\Windows\System32\winlogon.exe</Data> <Data Name="IpAddress">127.0.0.1</Data> <Data Name="IpPort">0</Data> </EventData> </Event>
Required Server Roles: None.
Minimum OS Version: Windows Server 2008, Windows Vista.
Event Versions: 0.
Field Descriptions:
Subject:
-
Security ID [Type = SID]: SID of account that reported information about logon failure. Event Viewer automatically tries to resolve SIDs and show the account name. If the SID cannot be resolved, you will see the source data in the event.
[!NOTE]
A security identifier (SID) is a unique value of variable length used to identify a trustee (security principal). Each account has a unique SID that is issued by an authority, such as an Active Directory domain controller, and stored in a security database. Each time a user logs on, the system retrieves the SID for that user from the database and places it in the access token for that user. The system uses the SID in the access token to identify the user in all subsequent interactions with Windows security. When a SID has been used as the unique identifier for a user or group, it cannot ever be used again to identify another user or group. For more information about SIDs, see Security identifiers. -
Account Name [Type = UnicodeString]: the name of the account that reported information about logon failure.
-
Account Domain [Type = UnicodeString]: subject’s domain or computer name. Here are some examples of formats:
-
Domain NETBIOS name example: CONTOSO
-
Lowercase full domain name: contoso.local
-
Uppercase full domain name: CONTOSO.LOCAL
-
For some well-known security principals, such as LOCAL SERVICE or ANONYMOUS LOGON, the value of this field is «NT AUTHORITY».
-
For local user accounts, this field will contain the name of the computer or device that this account belongs to, for example: «Win81».
-
-
Logon Type [Type = UInt32]: the type of logon that was performed. «Table 11. Windows Logon Types» contains the list of possible values for this field.
Table 11: Windows Logon Types
Logon Type Logon Title Description 2 Interactive A user logged on to this computer. 3 Network A user or computer logged on to this computer from the network. 4 Batch Batch logon type is used by batch servers, where processes may be executing on behalf of a user without their direct intervention. 5 Service A service was started by the Service Control Manager. 7 Unlock This workstation was unlocked. 8 NetworkCleartext A user logged on to this computer from the network. The user’s password was passed to the authentication package in its unhashed form. The built-in authentication packages all hash credentials before sending them across the network. The credentials do not traverse the network in plaintext (also called cleartext). 9 NewCredentials A caller cloned its current token and specified new credentials for outbound connections. The new logon session has the same local identity, but uses different credentials for other network connections. 10 RemoteInteractive A user logged on to this computer remotely using Terminal Services or Remote Desktop. 11 CachedInteractive A user logged on to this computer with network credentials that were stored locally on the computer. The domain controller was not contacted to verify the credentials.
Account For Which Logon Failed:
-
Security ID [Type = SID]: SID of the account that was specified in the logon attempt. Event Viewer automatically tries to resolve SIDs and show the account name. If the SID cannot be resolved, you will see the source data in the event.
[!NOTE]
A security identifier (SID) is a unique value of variable length used to identify a trustee (security principal). Each account has a unique SID that is issued by an authority, such as an Active Directory domain controller, and stored in a security database. Each time a user logs on, the system retrieves the SID for that user from the database and places it in the access token for that user. The system uses the SID in the access token to identify the user in all subsequent interactions with Windows security. When a SID has been used as the unique identifier for a user or group, it cannot ever be used again to identify another user or group. For more information about SIDs, see Security identifiers. -
Account Name [Type = UnicodeString]: the name of the account that was specified in the logon attempt.
-
Account Domain [Type = UnicodeString]: domain or computer name. Here are some examples of formats:
-
Domain NETBIOS name example: CONTOSO
-
Lowercase full domain name: contoso.local
-
Uppercase full domain name: CONTOSO.LOCAL
-
For some well-known security principals, such as LOCAL SERVICE or ANONYMOUS LOGON, the value of this field is «NT AUTHORITY».
-
For local user accounts, this field will contain the name of the computer or device that this account belongs to, for example: «Win81».
-
-
Logon ID [Type = HexInt64]: hexadecimal value that can help you correlate this event with recent events that might contain the same Logon ID, for example, «4624: An account was successfully logged on.»
Failure Information:
-
Failure Reason [Type = UnicodeString]: textual explanation of Status field value. For this event, it typically has «Account locked out» value.
-
Status [Type = HexInt32]: the reason why logon failed. For this event, it typically has «0xC0000234» value.
-
Sub Status [Type = HexInt32]: additional information about logon failure.
[!NOTE]
For more information about various Status or Sub Status codes, see NTSTATUS Values.
Process Information:
-
Caller Process ID [Type = Pointer]: hexadecimal Process ID of the process that attempted the logon. Process ID (PID) is a number used by the operating system to uniquely identify an active process. To see the PID for a specific process you can, for example, use Task Manager (Details tab, PID column):

If you convert the hexadecimal value to decimal, you can compare it to the values in Task Manager.
You can also correlate this process ID with a process ID in other events, for example, «4688: A new process has been created» Process InformationNew Process ID.
-
Caller Process Name [Type = UnicodeString]: full path and the name of the executable for the process.
Network Information:
-
Workstation Name [Type = UnicodeString]: machine name from which logon attempt was performed.
-
Source Network Address [Type = UnicodeString]: IP address of machine from which logon attempt was performed.
-
IPv6 address or ::ffff:IPv4 address of a client.
-
::1 or 127.0.0.1 means localhost.
-
-
Source Port [Type = UnicodeString]: source port that was used for logon attempt from remote machine.
- 0 for interactive logons.
Detailed Authentication Information:
-
Logon Process [Type = UnicodeString]: the name of the trusted logon process that was used for the logon attempt. See event «4611: A trusted logon process has been registered with the Local Security Authority» description for more information.
-
Authentication Package [Type = UnicodeString]: The name of the authentication package that was used for the logon authentication process. Default packages loaded on LSA startup are located in «HKLMSYSTEMCurrentControlSetControlLsaOSConfig» registry key. Other packages can be loaded at runtime. When a new package is loaded a «4610: An authentication package has been loaded by the Local Security Authority» (typically for NTLM) or «4622: A security package has been loaded by the Local Security Authority» (typically for Kerberos) event is logged to indicate that a new package has been loaded along with the package name. The most common authentication packages are:
-
NTLM – NTLM-family Authentication
-
Kerberos – Kerberos authentication.
-
Negotiate – the Negotiate security package selects between Kerberos and NTLM protocols. Negotiate selects Kerberos unless it cannot be used by one of the systems involved in the authentication or the calling application did not provide sufficient information to use Kerberos.
-
-
Transited Services [Type = UnicodeString] [Kerberos-only]: the list of transmitted services. Transmitted services are populated if the logon was a result of a S4U (Service For User) logon process. S4U is a Microsoft extension to the Kerberos Protocol to allow an application service to obtain a Kerberos service ticket on behalf of a user – most commonly done by a front-end website to access an internal resource on behalf of a user. For more information about S4U, see https://msdn.microsoft.com/library/cc246072.aspx
-
Package Name (NTLM only) [Type = UnicodeString]: The name of the LAN Manager subpackage (NTLM-family protocol name) that was used during the logon attempt. Possible values are:
-
«NTLM V1»
-
«NTLM V2»
-
«LM»
Only populated if «Authentication Package» = «NTLM».
-
-
Key Length [Type = UInt32]: the length of NTLM Session Security key. Typically, it has a length of 128 bits or 56 bits. This parameter is always 0 if «Authentication Package» = «Kerberos», because it is not applicable for Kerberos protocol. This field will also have «0» value if Kerberos was negotiated using Negotiate authentication package.
Security Monitoring Recommendations
For 4625(F): An account failed to log on.
[!IMPORTANT]
For this event, also see Appendix A: Security monitoring recommendations for many audit events.
-
If you have a pre-defined «Process Name» for the process reported in this event, monitor all events with «Process Name» not equal to your defined value.
-
You can monitor to see if «Process Name» is not in a standard folder (for example, not in System32 or Program Files) or is in a restricted folder (for example, Temporary Internet Files).
-
If you have a pre-defined list of restricted substrings or words in process names (for example, «mimikatz» or «cain.exe«), check for these substrings in «Process Name.»
-
If SubjectAccount Name is a name of service account or user account, it may be useful to investigate whether that account is allowed (or expected) to request logon for Account For Which Logon FailedSecurity ID.
-
To monitor for a mismatch between the logon type and the account that uses it (for example, if Logon Type 4-Batch or 5-Service is used by a member of a domain administrative group), monitor Logon Type in this event.
-
If you have a high-value domain or local account for which you need to monitor every lockout, monitor all 4625 events with the «SubjectSecurity ID» that corresponds to the account.
-
We recommend monitoring all 4625 events for local accounts, because these accounts typically should not be locked out. Monitoring is especially relevant for critical servers, administrative workstations, and other high-value assets.
-
We recommend monitoring all 4625 events for service accounts, because these accounts should not be locked out or prevented from functioning. Monitoring is especially relevant for critical servers, administrative workstations, and other high value assets.
-
If your organization restricts logons in the following ways, you can use this event to monitor accordingly:
-
If the «Account For Which Logon Failed Security ID» should never be used to log on from the specific Network InformationWorkstation Name.
-
If a specific account, such as a service account, should only be used from your internal IP address list (or some other list of IP addresses). In this case, you can monitor for Network InformationSource Network Address and compare the network address with your list of IP addresses.
-
If a particular version of NTLM is always used in your organization. In this case, you can use this event to monitor Package Name (NTLM only), for example, to find events where Package Name (NTLM only) does not equal NTLM V2.
-
If NTLM is not used in your organization, or should not be used by a specific account (New LogonSecurity ID). In this case, monitor for all events where Authentication Package is NTLM.
-
If the Authentication Package is NTLM. In this case, monitor for Key Length not equal to 128, because all Windows operating systems starting with Windows 2000 support 128-bit Key Length.
-
If Logon Process is not from a trusted logon processes list.
-
-
Monitor for all events with the fields and values in the following table:
Field Value to monitor for Failure InformationStatus or
Failure InformationSub Status0XC000005E – «There are currently no logon servers available to service the logon request.»
This issue is typically not a security issue, but it can be an infrastructure or availability issue.Failure InformationStatus or
Failure InformationSub Status0xC0000064 – «User logon with misspelled or bad user account».
Especially if you get several of these events in a row, it can be a sign of a user enumeration attack.Failure InformationStatus or
Failure InformationSub Status0xC000006A – «User logon with misspelled or bad password» for critical accounts or service accounts.
Especially watch for a number of such events in a row.Failure InformationStatus or
Failure InformationSub Status0XC000006D – «This is either due to a bad username or authentication information» for critical accounts or service accounts.
Especially watch for a number of such events in a row.Failure InformationStatus or
Failure InformationSub Status0xC000006F – «User logon outside authorized hours». Failure InformationStatus or
Failure InformationSub Status0xC0000070 – «User logon from unauthorized workstation». Failure InformationStatus or
Failure InformationSub Status0xC0000072 – «User logon to account disabled by administrator». Failure InformationStatus or
Failure InformationSub Status0XC000015B – «The user has not been granted the requested logon type (aka logon right) at this machine». Failure InformationStatus or
Failure InformationSub Status0XC0000192 – «An attempt was made to logon, but the Netlogon service was not started».
This issue is typically not a security issue but it can be an infrastructure or availability issue.Failure InformationStatus or
Failure InformationSub Status0xC0000193 – «User logon with expired account». Failure InformationStatus or
Failure InformationSub Status0XC0000413 – «Logon Failure: The machine you are logging onto is protected by an authentication firewall. The specified account is not allowed to authenticate to the machine».
